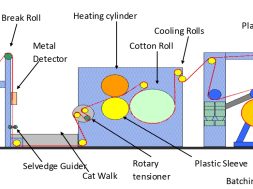
Lab-dip Preparation in Textile Industry
Lab-dip Preparation in Textile Industry
Lab–dip can be described as one kind of swatch board containing buyers sample, shaded
swatch & also fabric and all dyeing parameters including chemical names. Lab-dip
machines are used in this operation. To produce a lab-dip at first a standard recipe of the
given sample is produced by computer color matching system and with that recipe a trial
batch is dyed & matched with the standard. After approval, the recipe is then sent for bulk
production with the sample.
Stock Solution Making
In laboratory operations, the amount of sample processed is relatively small-scaled in
comparison with the bulk production. The amount of chemicals required is too small to
weight out with proper accuracy with regular available balances and it is even more
difficult to redo the same procedure with any degree of precision. In order to measure
chemicals accurately, stock solutions of dyes and other ingredients are prepared and the
required volumes are measured out accurately into the dyebath.
For example,
- 1 g of dye dissolved in 200 ml of water gives a 0.5% stock solution.
- For each 1 g of fibre, 0.01 g of dye is required to provide a 1% shade (o.w.f.).
- 0.01 g of dye is contained in ml of stock solution.
- Therefore for every 1 g of fibre, 2 ml of stock solution will be required to produce a 1%
shade. - The same reasoning applies to other additives; for example, the composition of 10% Glauber’s salt, based on the mass of fibre, is calculated in the same way as a 10%
shade of dye.
The below general formula may be used for representing the amount of stock dye solution required:

In this way the required volumes of dye solution and other additives may be calculated,
added together and subtracted from the total volume of dyebath to obtain the amount of
water required.
Also, if the color or chemical dosage is given in grams per liter, the following formula can be used:


Fig : Stock solutions
General salt and soda dosage for different types of dyes: For Novacron FN/S/NC/Remazol RGM and others .
Salt-Soda dosage for Novacron FN/S/NC/Remazol RGM and others
| Shade% | <0.1% |
0.1% – 0.25% |
0.25%- 0.5% |
0.5%- 1.0% |
1.0%- 2.0% |
2.0%- 3.0% |
|||||
|
Glauber ‘s salt (g/L) |
10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | |||||
| Soda (g/L) | 08 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | |||||
| Shade% | 3.0%-4.0% |
4.0%- 5.0% |
Above 5% | Extra deep/ Black | |||||||
|
Glauber ‘s salt (g/L) |
60 | 70 | 80 | 100 | |||||||
| Soda (g/L) | 20 | 20 | 20 | Soda: 5 |
Caustic soda: 1.5 |
||||||
- Salt stock solution: 30%
- Soda Stock solution: 15%
- Caustic soda stock solution: 10%
- Liquor ratio: 1:7
Lab dip processes
Dyeing process 100% cotton knit fabric with RR dyes
- Recipe preparation for dyeing that matches the buyer given swatch using a spectrophotometer
- Stock solution preparation for required dyes and auxiliaries
- Weighing fabric sample and dye bath preparation adding sequestering agent, dyes, leveling agent and salt into water by digital pipetting, maintain a total 1:5 M:L ratio, salt exhaustion at 40°C
- Raising temperature up to 60°C and alkali dosing
- Running machine in 60°C for 60 minutes
- Cooling down to 50°C and cold wash at room temperature
- Neutralization with 0.5 g/l acetic acid and cold wash
- Hot wash at 90°C for 10 minutes using 1g/l soaping agent
- Cold wash at room temperature and bath drop
- Fabric unloading

Dyeing process 100% cotton knit fabric with RGB dyes
Dyeing process of RGB dyes is similar to dyeing process of RR dyes except for the fact that in dyeing with RGB dyes, alkali dosing is done in the dye bath just before raising the temperature up to 60°C.

Dyeing process 100% cotton knit fabric with Turquoise blue dyes
- Recipe preparation for dyeing that matches the buyer given swatch using a spectrophotometer
- Stock solution preparation for required dyes and auxiliaries
- Weighing fabric sample and dye bath preparation adding sequestering agent, dyes, leveling agent and salt into water by digital pipetting, maintain a total 1:5 M:L ratio, salt exhaustion at 40°C
- Raising temperature up to 90°C and keeping it for 20 minutes
- Cooling at 60°C and alkali dosing
- Running machine in 60°C for 60 minutes
- Cooling to 50°C and cold wash at room temperature
- Neutralizing with 1g/l acetic acid and cold wash
- Hot wash at 90°C for 10 minutes using 1g/l soaping agent
- Cold wash at room temperature and bath drop
- Fabric unloading

Dyeing process of polyester fabrics using disperse dyes
- Recipe preparation for dyeing that matches the buyer given swatch using a spectrophotometer
- Stock solution preparation for required dyes and auxiliaries
- Weighing fabric sample and dye bath preparation adding sequestering agent, dyes and leveling agent into water by digital pipetting, maintain a total 1:5 M:L ratio
- Adding 1.25 g/l acetic acid to maintain a 4.5 pH of the dye bath
- Raising temperature up to 1300C
- Running machine for 30 min for light shade(<0.5%), 45 min for medium shade (0.5%– 1.5%) and 60 min for dark shade(>1.5%)
- Cooling to 50°C and cold wash at room temperature
- Raising temperature up to 800C
- Reduction clearing with caustic soda and hydrous for 10 mins with the following dosage:
0.5 g/l + 0.5g/l for light shade, 1 g/l + 1g/l for medium shade, 2g/l + 2g/l for dark shade
- Cold wash at room temperature
- Neutralization with 0.5 g/L acetic acid at room temperature and cold wash 12. Fabric unloading

Blend dyeing
The individual dyeing of polyester with disperse dyes and cotton with reactive dyes combined is the process called blend dyeing. Blend dyeing consists of reserve shades, namely single part dyeing, solid shades, namely double part dyeing and cross shades in which cotton and polyester are dyed in two different shades to enhance the aesthetic properties of the fabric.
For a double part dyeing of CVC knit fabric, at first the buyer-given sample is assessed spectrophotometrically and dye (%) needed to match the cotton part of the fabric is identified. The cotton part is then carbonized with 70% sulfuric acid at 38°C for 20 minutes. After carbonizing, the PES skeleton that remains is rinsed, dried and weighed.
The color of which is also matched spectrophotometrically, giving the recipe of dyes (%) needed to match the shade for PES. According to the percentage weights of fibers in the fabric, the recipe for individually dyeing the components is adjusted where only the dye (%) and amount of levelling agent to use changes for the blend fabric.
(285)