Eco-Friendly Textile Dyeing Process
Eco-Friendly Textile Dyeing Process
Introduction:
Dyeing and finishing processes in the textile industry have attracted a lot of attention lately as the concept of sustainable and eco-friendly textiles and garments are gaining popularity. Here we will focus today on eco-friendly textile methods which are a widely discussed topic for the present.
The textile industry is the second largest polluting industry in the world. For centuries, the global textile industry has been working to strike a balance between economic development and environmental protection. That is why the use of water resources and environmental protection in textile production has become a major concern. Conventional dyeing methods require a lot of water and most of the toxic waste mixes with the water to contaminate the water which is harmful to the environment and in this case the cost of processing for recycling water is also very high. Besides, due to the toxicity of dyes and chemicals used in textile dyeing and improper disposal of such wastes, many workers have developed skin diseases and respiratory problems. And this can be made possible by the use of chemical-free dyeing and the assimilation of environmental processes.
The synthetic dyes used in textile dyeing are thought to be responsible for about 20 per cent of the world’s water pollution. The main contributors to this problem are the use of non-biodegradable petroleum-based colourants for dyeing textiles, toxic agents used in colour fixing in textiles and the release of these coolants and fixation agents in our surrounding ecosystems. Because of these problems, the dyeing industry is now looking for new methods of garment dyeing that will be environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Some sustainable dyeing methods invented for eco-friendly textile dyeing:
Currently, the textile dyeing industry favours the use of halogen and heavy metal-free, very high extraction and fixation value dyes. Some of the newly invented dyeing methods are discussed below:
Use of natural dyes:
We all know that natural dyes or natural dyes are environmentally friendly. Natural pigments have anti-bacterial (anti-bacterial) and anti-fungal (anti-fungal) properties. This is why dyeing clothes with natural dyes reduces the attack of bacteria and fungi which protects the wearer from various diseases. Natural pigments are usually made using plants (fruits, bark, stems), algae, minerals, bacteria, fungi, marine animals such as starfish and are substituted for synthetic or synthetic pigments and have medicinal properties. Nowadays, colouring from different types of fruits is gaining popularity.
For example, the colouring method of cotton fabric from watermelon extract has been successful. It is an environmentally friendly cotton colouring method. This method consumes relatively less energy and requires less chemical helper. Thus the use of natural dyeing can drive the development of herbal dyeing methods in the textile dyeing industry and this method is not only bio-degradable but also helps in making anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic fabrics.

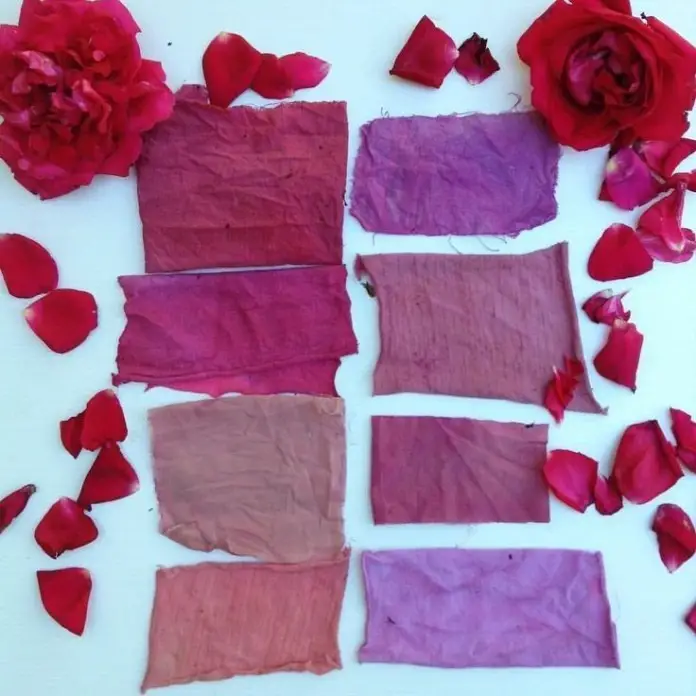
Fig : Fabric colouring with rose petals
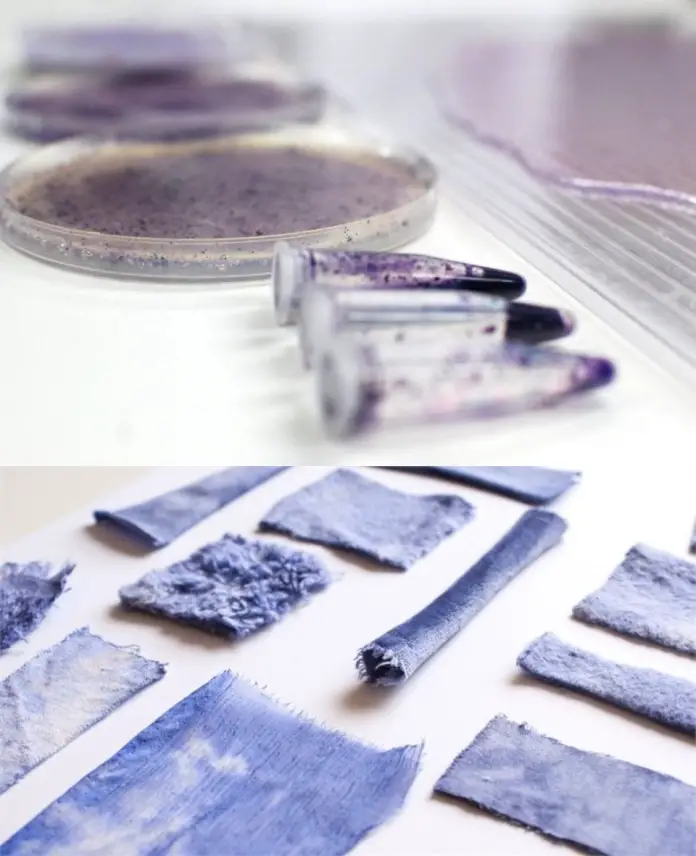

Fig : Colours made from bacteria
Hybrid Pigment:
Eco-foot has created an unimaginable colouration industry by chemically combining polymer particles and pigments to create a hybrid pigment that can react with cellulose fibres at temperatures up to 250 C. With this hybrid pigment, garments made of cotton can be easily dyed at low temperatures. With this, it is possible to dye the wool more ecologically. In this technology, dyeing will be possible without the use of salt. Eco foot has also discovered some dyeing aids that are capable of preventing the hydrolysis of pigments during dyeing processing. This eliminates the need for a hard-washing process to remove the hydrolyzed pigment. This will save about 50 per cent of the water used in hybrid pigments and dyeing aids that were used during the preparation and dyeing process.
Use of Powder Dyes from Textile Fibre:
An Italian company, Officina +39 (officinal + 39), has come up with a new invention of sustainable dyeing, a durable range of dyes (resicrome) made from textile scrap, fibre material and recyclable clothing. Although most dyes are used as chemical solutions, resistome is applied as a suspension. This facilitates water filtration and reduces environmental impact.
Cotton Pre-Treatment:
For cotton pre-treatment, about 200 litres of water is required for dyeing 1 kg of fabric. That is why a new cotton pre-treatment method has been invented where cotton is pre-treated with a cationic reagent called ECO-FAST Pure. Using this apparent technology, it is possible to reduce the amount of water used in the cotton dyeing process by as much as 50 per cent. Pre-treated cotton with Eco-Fast Pure has higher pigment retention capacity and does not require any fixation chemicals to retain the pigment. In this way, it is estimated that it is possible to reduce the use of toxic chemicals by 95 per cent.
Engineered microorganisms:
This method modifies the bacteria in a way that plays an important role in textile colouration and reduces the amount of water used in this method by 10 times the traditional method. A team of researchers from the University of California has developed a denim dice called indican using E. coli bacteria that can be easily converted to indigo through enzymatic treatment.
Some new innovative dye and auxiliaries:
Hustman Textile Effects has developed the ‘Avitera’, a row of polyreactive dice made of cotton that can form fibrous bonds faster than conventional reactive dice.
It could dramatically reduce water and energy consumption by about 50 per cent.
Univadine E3-3D, a dyeing aid that enhances the diffusion of dye into polyester, is free of hazardous chemicals that are made following current and expected industrial durability standards.
Carbon dioxide dyeing (CO2 dyeing) – a sustainable dyeing method:
A game-changer for supercritical fluid dyeing or carbon dioxide dyeing sustainable dyeing. It does not require any water or effluent. For many textile producing countries, the scarcity of water and its accompanying material has become increasingly difficult. The supercritical carbon-dioxide dyeing method uses less water and energy than the conventional dyeing method and also takes less time for dyeing. On the other hand, in the case of polyester dyeing, if this carbon-dioxide dyeing method is used with Disperse dye, very good dye fixation and levelling are obtained without structural agents or auxiliaries. It is non-toxic compared to the solvent dyeing method and it can be widely recycled.
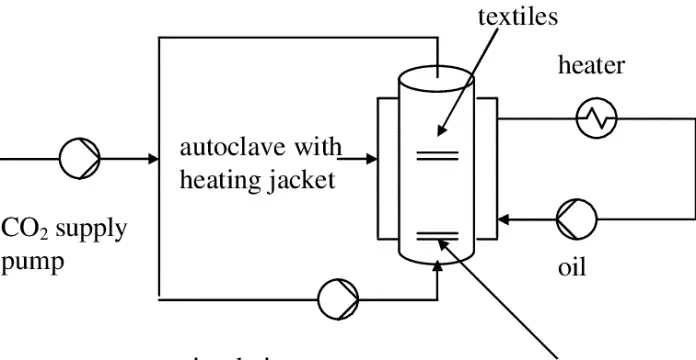
Fig : Carbon-dioxide dyeing method
Conclusion:
Innovations in the textile dyeing sector are very promising and environmentally friendly but still have many obstacles to overcome. Cold dyeing, dry heat fixation, and vegetable tanning are some of the processes that textile manufacturers can use to develop eco-friendly garments. Can play an important role in reducing usage.
Resources:
- https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/7250/eco-textile-dyeing-and-finishing
- https://bunon.info/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324214252_Eco-friendly_dyes_and_dyeing_You_may_download_the_paper_from_the_following_link_httpsciedtecheujournalsadvmtenvscicurrent-issue
(750)