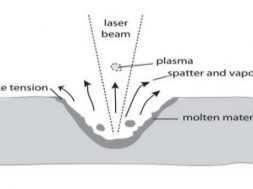
Laser in Denim Industry | Classification of Laser Technology
Laser in Denim Industry | Classification of Laser Technology
Classes of Lasing Media :
A substance, which can be excited by input energy, is called a lasing media. The lasing media have the ability to stay in a metastable state. It is generally transparent to light. The substance used as lasing media can be a solid, gas, liquid dye or semiconductor. Solid lasing media is used for producing solid-state laser. Due to the high density of lasing atoms, solid-state lasers can generate higher power output per unit volume compared to the gaseous-state lasers. A single gas or gaseous mixture can be used to produce gaseous-state lasers. Gaseous-state lasers are produced by passing the electric discharge in the gaseous lasing medium. The most common type of gaseous laser is produced from helium-neon (He-Ne). This laser is mainly used in teaching laboratories, at construction sites and supermarkets. Liquid dyes can also produce laser by using ultraviolet (UV) light. These liquid dyes can be prepared by dissolving the solid dye particles in suitable solvent. The dyes and sol¬ vents with similar energy levels are selected, that help to form a continuum for achieving high energy output with wavelengths of visible light. Better tunability is the unique feature of a dye laser, which distinguishes it from the solid laser. A single dye produces a single wavelength whereas dyes can be mixed to obtain a range of wavelengths. Semiconductors can also
be used to produce laser with the help of electric discharge. These lasers are characterized by their efficiency, miniature size and durability.
Laser Classification Based on Hazards :
Since the early 1970s, lasers were being classified into four classes and some subclasses depending on their wavelength and maximum output power. This classification was based on the severity of the damage to a person when exposed to laser. These classes can be from 1 to 4. A Class 1 laser is absolutely not dangerous when used, whereas the Class 4 laser is the most dangerous. The existing system was the revised system since 2002, prior to that the old system was used. In the new system amendments have been done to certain types of lasers having a lower hazard than mentioned in the old system. Based on the output power in a specific wavelength, lasers are classified. It is essential the correct information on the laser class, potential hazards and safety instructions are specified by the equipment manufacturers. In the classes 1 -4 laser, there are the sub-classes 1M, 2M, 3A and 3B. The new system currently in use (shown in Table 1) uses Arabic numerals (1-4), whereas it was classified with Roman numerals (I-IV) in the old system.
Classification Based on Generating Media :
Based on the generating media, lasers can be classified into three groups:
- carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers,
- neodymium (Nd) lasers
- neodymium yttrium-aluminium-garnet (Nd-YAG) lasers . The CO2 lasers can be used for boring, cutting and engraving .
1 . CO2 lasers can be of the four types:
- fast axial flow,
- slow axial flow,
- transverse flow and
- slab lasers . In fast axial flow, a mixture of CO2, nitrogen (N2) and helium (He) is used at high speed by a turbine.
The new system for laser classification :
Laser class Features and Nature of hazards and precautions for various classes of lasers :
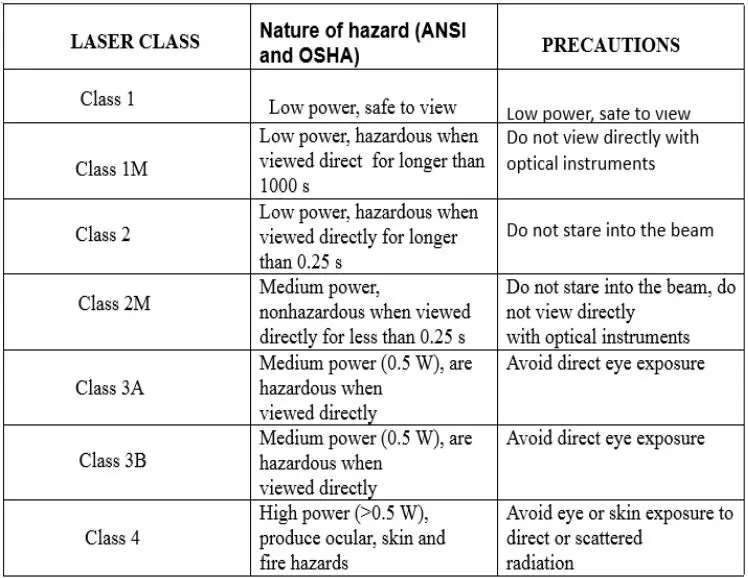
The Nd lasers and Nd-YAG lasers, although similar in style, they are applied in different areas. The former is used for boring, whereas the later is used for engraving. All the laser classes can be used for welding.
Generally, CO2 lasers are produced by passing the electric discharge through a gaseous mixture excited by direct current (DC) with radio frequency (RF) energy. This method is widely used as the DC-excited designs need electrodes inside the cavity, due to risk of erosion. Industrial cutting of steel, aluminium, paper, plastics, wood, and fabrics can be performed by CO2 lasers. For cutting metals and ceramics; and scribing Nd-YAG lasers are used.
The laser generator and external optics need cooling while in use (Choudhury and Shirley 2010). This can be achieved by a coolant such as water by circulating through a chiller in the laser equipment. The use of water cools the material and removes the debris. In addition, it helps to achieve parallel kerf and multi-directional cutting at high dicing speeds.
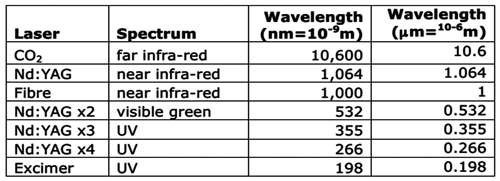
Another type of solid-state laser known as “fiber laser” is now becoming popular in metal cutting industry. This laser is produced from a solid gain medium without the use of any liquid or gas. The major advantage of fiber laser is the extremely small spot size. Fibre lasers, with a wavelength of 1.064 pm, can produce an extremely small spot size, which makes it ideal for cutting reflective metals.
The different laser systems according to their wavelength are as below :
Designing more environmentally friendly denim :
Traditionally, a pair of jeans was faded by washing the material in a chemical bath. Now it can be done with a simple automated laser ray in a second. This is not just a procedural shift, but minimizes the use of chemicals, water and time.

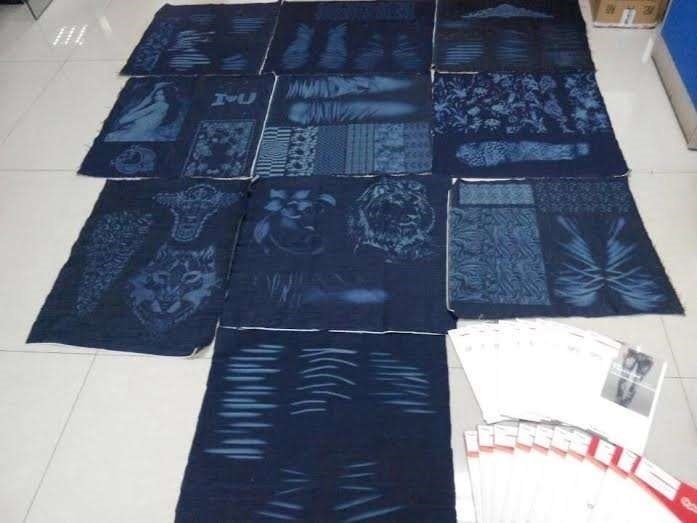
Fig 4: Different types of designs created using lasers
This allows the rate of production in a factory to increase, without impacting the quality of the product. The new technology also reduces the risks of accidents to the workers. With lower use of chemicals, there is lower likelihood of a toxic accident.
Consumers and buyers, especially from Europe, are increasingly concerned about the environment-friendly and water efficient aspects of the technology. This is nudging producers to take the new sustainable path.
You May Look on Below :
- Laser in Denim Industry | Classification of Laser Technology
- Laser in Denim Industry | Laser Finishing Method | Flow Chart Of Laser Finish
- Laser in Denim Industry | Advantages and Disadvantages of laser finish | Laser safety
- Laser in Denim Industry | Laser Finish is Safe | Lasers Are Sustainable
- Laser in Denim Industry | Laser Technology
(192)