Composite Fibers: A Modern Day Need
Composite Fibers: A Modern Day Need
It is quite clear to us that, in modern days, where efficiency is a prime concern in the field of engines and machines, composite and light-weight fibers are playing a significant role in creating light-weight body parts of vehicles and transports. Their special insulating properties along with stiffness has allowed them a favorable position above most metals. In our daily life, we use many utilities which have these composite fibers in their composition, e.g:polyester_acrylic,carbon-kevlar(body armor),etc. Starting from airplane to concord parts, composite fibers are covering major sectors of the mechanical world.

Composites are created by combining two or more materials to produce a new material.Talking of composite fibers, many common names come to rise. Epoxy, meta-aramids, carbon nanotube,etc. are some vital elements of composite fiber production. Properties of composites like stiffness, thermal expansion etc. can be varied continuously over a broad range of values using appropriate fiber, epoxy resin and fabrication mechanism.

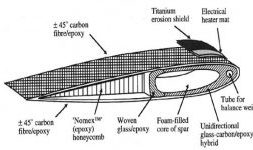
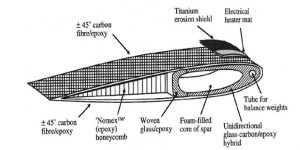
Fig : Schematic section through a typical composite construction for a helicopter rotor blade ( Courtesy of Westland helicopter )
Epoxy: Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. Epoxy resins may be reacted (cross-linked) either with themselves through catalytic homopolymerisation, or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines, acids (and acid anhydrides), phenols, alcohols and thiols. These co-reactants are often referred to as hardeners or curatives, and the cross-linking reaction is commonly referred to as curing. Reaction of polyepoxides with themselves or with polyfunctional hardeners forms a thermosetting polymer, often with high mechanical properties, temperature and chemical resistance. Epoxy has a wide range of applications, including metal coatings, use in electronics / electrical components, high tension electrical insulators, fiber-reinforced plastic materials and structural adhesives.
There are 3 types of composites mainly :
1 . Metal matrix composite (MMC) : The reinforcement can either be continuous, or discontinuous. Discontinuous MMC can be isotropic, can be worked with standard metalworking techniques, such as extrusion, forging or rolling. In addition, they may be machined using conventional techniques, but commonly would need the use of polycrystalline tooling(PCT)

Fig : Microscopic structure of a lightweight reinforced alumina fibers
2 . Ceramic matrix composite(CMC) : They consist of ceramic fibers embedded in ceramic matrix, thus forming a ceramic fiber reinforced ceramic(CFRC) material. Examples are carbon –carbon nanofibers, carbon-SiC fibers,etc.

Fig:Typical composite made out of ceramic
3 . Polymer matrix composite(PMC): It is also referred as fiber-reinforced plastics(FRP). In these composites, plastic is reinforced by fibers to make ot light and strong. The matrix is resonated plastic. Basically these are epoxy, polyester, vinyl ester and polypropylene.
There are multiple uses of composite fibers. Carbide drills are often made from a tough cobalt matrix with tungsten carbide particles inside. Alumunium-SiC composite fibers are used in bicycles.
Fiber reinforced plastics are best suited for any design program that demands weight savings. Carbon nanotubes are used in medical science, in order to make cancer treatment successful. Carbon fibers are also very light and strong materials. PMC fibers play a vital role alongside duralumin in order to produce plane parts successfully.
(35)