Textile Printing
Textile Printing
Printing is a technique of producing desired patterns (design) on textile fabrics by use of selected dyes or pigments. Printing involves localized coloration. This is usually achieved by applying thickened pastes containing dyes & pigments onto the fabric surface according to a given color design. The main object of printing is the production of attractive designs with well defined boundaries in one or more colors. In other words, dyes and pigments are applied locally or discontinuously to produce the various designs. In fact. Printing is described as localized dyeing. In the Unit-2 of Azad Rifat Fibers (Pvt.) Ltd.. there is a small printing unit which does some of the in-house job with two rotary screen printing machines and also with hand screen printing.
List of machines in the printing section
- Rotary screen printing machine
- Steamer
- Exposure machine
Types of printing
Different types of print are done in the hand screen printing section which give different aesthetic appeal –
- Pigment print
- Discharge print
- Rubber print
- Glitter/ metallic color print
- Foil print
- Photo print
- Radium print
Process flow of printing
Design obtained from swatch send by the buyer
↓
Design selection and color separation
↓
Production of design repeats by using software
↓
Preparation of screen
↓
Placing the fabric on the printing table
↓
Print paste is prepared
↓
Print paste application on the fabric
↓
Curing/Steaming the fabric at required temperature
↓
Washing
↓
Finishing
Screen preparation
The designer creates or makes modifications to the design supplied by the buyer. This may be a hard copy or a soft copy (it is easier to work with the latter). Generally Adobe Photoshop is Used for designing. The designer highlights the number of colors needed, the screen dimensions for the repeat that was created and the mesh number depending on the coverage of the print. The designer also highlights the type of print, type of fabric, fabric width and GSM, on which the printing will be done. The mesh fabric required for the print is selected and mounted on the frame using adhesive and is dried. Once the screen mesh has been applied and dried, the screen (of 94 specified dimensions) is coated with a photosensitive emulsion using an automatic coating machine. Generally two strokes are given to evenly distribute the emulsion. Then the coated screen is left to dry for several minutes. As it dries, the areas of the design that are drawn with black ink is opaque and doesn’t pass light resulting in solidifying the photosynthetic chemical. After exposure to light, the the screen is washed where the black inked areas can easily be removed using low-pressure water sprays. The screen is now ready for use for flat screen printing purposes.

Fig : Print screen preparation
In the hand screen printing, Mesh number (threads per cm) is selected on the basis of design, type of print, coverage, print paste viscosity etc. High mesh numbers are selected for fine outlines and prints, whereas low mesh numbers are used for TiO2 prints, glitter prints etc. All screens have the design number, buyer/party name and number of colors to be printed included in the screen.

Fig : Hand screen printing
For pigment print, only pigment, binder and synthetic thickener is used. Curing is done at 130°C for 20 – 30 seconds. For discharge, the print paste contains the discharging agent, white pigment and binder for white discharge, and colored pigment and binder for color discharge. Curing is done at 160°C for 60 seconds under hot air. For rubber print, a high density water based rubber paste is used and is done at 140°C. For colored prints, the clear paste is used and for white prints the white paste is used .Glitter prints involve using a gloss binder/ metallic binder, glitter ) and then curing proceeds.

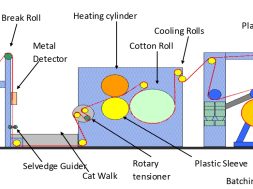
Fig : Rotary screen printing machine
(54)