Drafting system of roving frame I Draft Distribution of Speed or roving Frame |The simplex/roving frame is a necessary evil
Drafting system of roving frame | Draft Distribution of Speed or roving Frame | The simplex/roving frame is a necessary evil :
Speed Frame Sections
A standard type of a speed frame has following sections:
❶ Creel section
❷ Drafting section
❸ Twisting section
❹ Winding section
Creel section
Creel is the place situated at the back of the machine where the raw material is placed to be fed to the drafting zone.
The draw frame sliver cans are arranged in four or six rows in the creel zone.
Since the fibers in the drawn sliver have less coherence so it is necessary to keep the surface speed of the guide rollers equal to the surface speed of the back drafting rollers so that any false drafting may be avoided that can damage the sliver.
In modern fly frames, the creel transport rollers are arranged without vertical supporting rods, and these types of creels are called telescopic creels.
Just before the drafting section a photo-electric stop motion is used which detects the presence of the sliver and as the sliver breaks it automatically stops the machine.
Drafting section/Drafting system
The drafting section of the roving frame may be 3 over 3 or 4 over 4 with or without apron roller arrangement. Only the 3-over-3 or 4 over 4 roller with double apron drafting system are still to be found in modern machines offered by manufacturers. In general 3/3 drafting system is used, but for higher draft applications 4/4 drafting system is used. The draft often has limits not only at the upper limit (15 to 20), but also at lower limit. It is around 5 for cotton and 6 for synthetic fibers.
3-over-3 double apron drafting system:

❶ In production of a roving, a 3-over-3 roller with double apron drafting system is commonly used to attenuate the sliver.
❷ In a system of three pairs of rollers, there are two drafting zones. The first or back zone is designated the “break draft,” while the second or front zone is called the “main draft”.
❸ A pair of endless aprons is positioned in the high-draft front zone and made to move at the surface speed of the middle-roller pair.
❹ As fibers enter the high-draft front zone, the aprons will hold them and assist in keeping them moving at the surface speed of the middle rollers, while preventing the short-fibers being dragged forward by those fibers nipped and accelerated by the front rollers.
❺ The magnitude of break draft is usually small, varying between 1.1 and 1.5; therefore the front draft (i.e. main draft) is responsible for the major part of the total attenuation desired.
❻ The total draft is defined as the ratio of the surface speed of the front rolls to the surface speed of the back rolls and is a product of the break draft and the main draft:

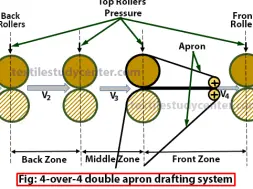
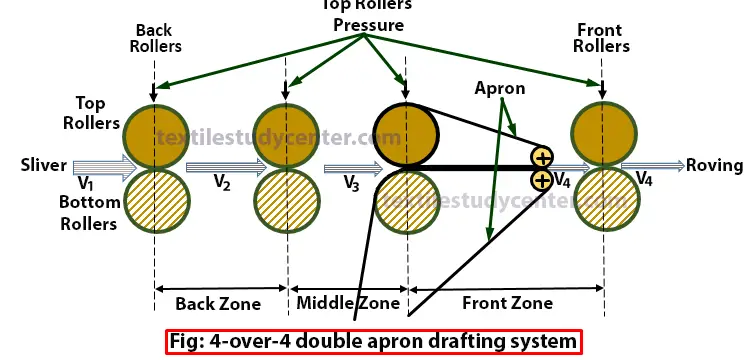
4-over-4 double apron drafting system:

❶ In 4-over-4 double apron drafting system, there are three drafting zones such as break draft, middle draft and front draft (or main draft).
❷ Back draft is apply in back zone which affects roving evenness. Less amount of draft is apply in middle zone where the condenser is used to condense sheet like sliver. Maximum amount of draft is apply in front zone where the apron is used to move at the surface speed of the middle-roller pair.
❸ The total draft is defined as the ratio of the surface speed of the front rolls to the surface speed of the back rolls and is a product of the break draft, middle draft and the main draft:

Draft distribution
An important consideration of the drafting zone is the draft distribution i.e. how much draft should be given in the back and front zones. In a 3-over-3 drafting system, there are two drafting zones such as break draft, and main draft. The first or back zone is designated the “break draft,” while the second or front zone is called the “main draft”. The total draft is the product of break and main draft. The break draft is in the range of 1.03 to 2.03 and all the remaining draft is given at the main drafting zone, generally ranging from about 5 to 18.
Table: Recommended total draft range

If the break draft is increased beyond an optimum value then the evenness of the spun yarn drastically reduces due to the formation of thick and thin places. It is recommended to keep the break draft as low as possible. The problems associated with the higher break draft than recommended are given as follows:
Requires higher drafting forces that can create vibrations in the back zone of the drafting system. Break draft may have to be as low as 1.022 to prevent roller vibrations.
Tends to create roving irregularities such as thick and thin places.
Table: Fiber and Machine Parameters Influencing Drafting Force

(11605)