Application of Medical Textiles | Healthcare / Hygiene Products
Medical Textile | Classification of Medical Textile | Application of Medical Textiles | Implantable Medical Textiles | Non-Implantable Medical Textiles | Extra-Corporal Devices | Healthcare / Hygiene Products
Application of Medical Textiles | Healthcare / Hygiene Products
Healthcare/Hygiene Products:
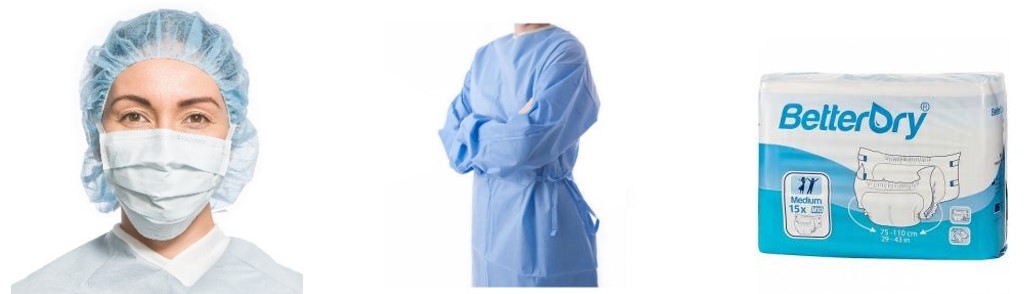
These products are related to daily uses in hospitals and health care industries. These include bedding, clothing, surgical gowns, cloths wipes and so on. All fibers are used in this product must be non-toxic, non-allergenic, noncarcinogenic and must be able to be sterilised without imparting any change in their physical or chemical characteristics. The range of this products available is vast but typically they are used in the operating room theatre or on the hospital ward for the hygiene, care and safety of staff and patients. Production of hygiene and medical textiles is on increase, as is the variety of applications in this important sector. By 2005, hygiene and medical textiles valued at US$4.1 billion, almost 12% of the global technical textiles market.

Fibres which are used for Healthcare/Hygiene Products:
|
Fiber type |
Application |
Fiber structure |
|
Cotton, polyester fibre, polypropylene fibre |
Surgical gowns |
Woven, nonwoven |
|
Viscose |
Surgical caps |
Nonwoven |
|
Viscose, polyester fibre, glass fibre |
Surgical masks |
Nonwoven |
|
Polyester fibre, polyethylene fibre |
Surgical drapes, cloths |
Woven, nonwoven |
|
Cotton, polyester fibre, polyamide fibre, elastomeric-fibre yarns |
Surgical hosiery |
Knitted |
|
Cotton, polyester fibre |
Blankets |
Woven, knitted |
|
Cotton |
Sheets, pillowcases |
Woven |
|
Polyester fibre, polypropylene fibre |
Protective clothing, incontinence, diaper/sheet, coverstock |
Nonwoven |
|
Viscose, lyocell |
Cloths/wipes |
Nonwoven |
|
Superabsorbent fibres, wood fluff |
Absorbent layer |
Nonwoven |
Surgical Masks:
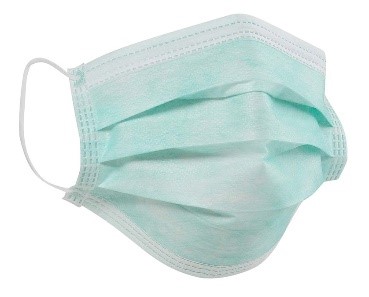
Surgical mask is intended to be worn by health professionals during surgery and during nursing to catch the bacteria shed in liquid droplets and aerosols from the wearer’s mouth and nose. Simple surgical masks protect wearers from being splashed in the mouth with body fluids, and prevent transmission of body fluids from the wearer to others, e.g. the patient. Surgical masks are popularly worn by the general public in East Asian countries to reduce the chance of spreading airborne diseases.
Surgical Drapes, Cloths:
These are also called scurbs. Scrubs are the sanitary clothing worn by surgeons, nurses, physicians and other workers involved in patient care in hospitals. Originally designed for use by surgeons and other operating room personnel. In many operating rooms, it is forbidden to wear any exposed clothing, such as a t-shirt, beneath scrubs. As scrubs are designed to promote a clean environment, the wearing of outside clothing is thought to introduce unwanted pathogens.

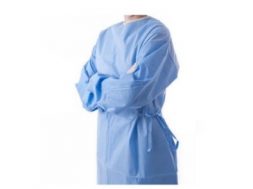
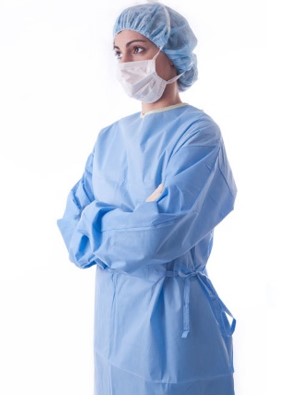
Surgical Gowns:
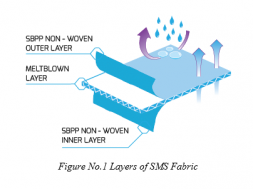
Surgical gowns used to help prevent the gown wearer from contaminating vulnerable patients, such as those with weakened immune systems. Gowns are one part of an infection-control strategy. Disposable nonwoven surgical gowns have been adopted to prevent the release of pollutant particles into the air which is a probable source of contamination to the patient. Surgical gowns are composed of nonwoven fabrics and polyethylene films in weight range of 30–45 g/m2.
Surgical Cap:
Surgical cap an accompaniment to the surgical gown (below) which covers the head, and sometimes facial hair, of members of the surgical team; the object is to avoid contamination of the wound. The surgical cap is in place to prevent hazardous bodily fluids from splashing onto the doctor or nurse’s hair and head. They are also used to prevent hair from affecting the vision of the medical professionals. On the other hand of the spectrum, loose hair or even other contaminants like hair products or dandruff is dangerous to the patient.

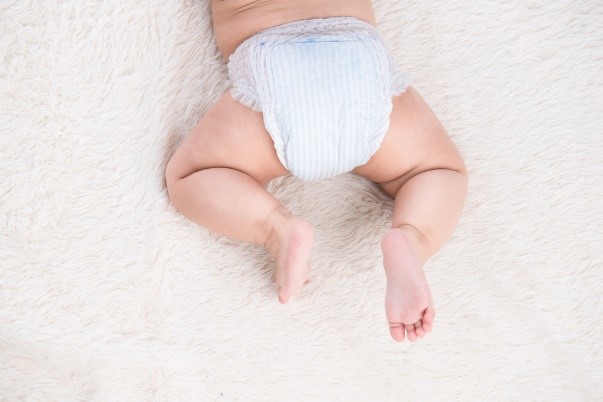
Diaper:
A diaper or a nappy is a type of underwear that allows the wearer to defecate or urinate without the use of a toilet, by absorbing or containing waste products to prevent soiling of outer clothing or the external environment. Diapers are made of cloth or synthetic disposable materials. Cloth diapers are composed of layers of fabric such as cotton, hemp, bamboo, microfiber, or even plastic fibers such as PLA or PU. Disposable diapers contain absorbent chemicals and are thrown away after use. Cloth diapers are reusable and can be made from natural fibers, synthetic materials, or a combination of both.

Medical textiles are located at the interfaces between technical disciplines and life sciences. Prospects for medical textiles are rather better, especially for nonwoven materials and disposable medical textiles used in surgical rooms. Combination of textile and its application in medical sciences has been proof that the painful days of patients and surgeons converting into the comfortable days.
Medical Textile | Classification of Medical Textile | Application of Medical Textiles | Implantable Medical Textiles | Non-Implantable Medical Textiles | Extra-Corporal Devices | Healthcare / Hygiene Products
(569)