Carbon Fibre | Properties of Carbon Fibre
Carbon Fibre | History of Carbon Fibre | Properties of Carbon Fibre | Production Process of Carbon Fibre
Carbon Fibre:
Carbon fibre shortly CF are fibres that have at least 90% of carbon in their mass. They are produced from carbonization of organic fibres.
There are 3 different types of CF:
- Graphite fibres hold 99% carbon in them: They are produced with graphitization (heating carbon fibres to a temperature higher then 2400 °C
- Carbon fibres which have at least 90% carbon (Carbonization and temperature higher then 1000 °C)
- Partially carbonised fibres which have less then 90% carbon, about 70-90% (Carbonization temperature 300-1200 °C)

History of Carbon Fibres:
1860 . Joseph Swan produced carbon fibres for the first time, for use in light bulbs.
1878 . First patent for carbon fibre that could be used in light bulbs by T.A. Edison
1879 . Thomas Edison baked cotton threads or bamboo slivers at high temperatures carbonizing them into an all-carbon fibre filament used in one of the first incandescent light bulbs to be heated by electricity.
1880 . Lewis Latimer developed a reliable carbon wire filament for the incandescent light bulb, heated by electricity.
1883 . Sir J.W. Swan patented the procedure of spinning acid solution of cellulose nitrate and development of carbon fibres from it
1963 . First commercial production of carbon fibres, patented by UK Ministry of Defence
1993 . Carbon Nano fibres CNF
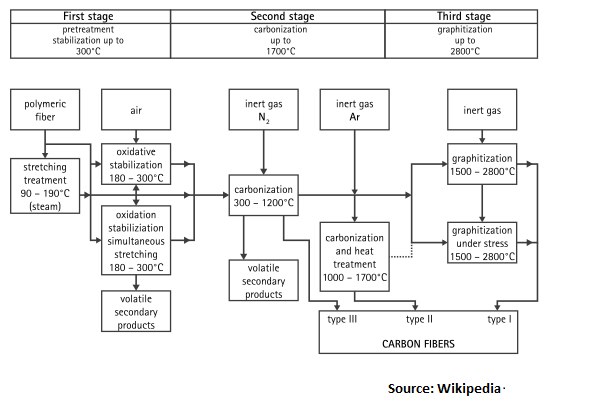
Production of Carbon Fibres with Pyrolysis from:
- Artificial organic fibers like viscose CV or Polyacrylonitrile PAN
- Resin after pyrolysis (cracking) oil and coal (mesophase pitch)
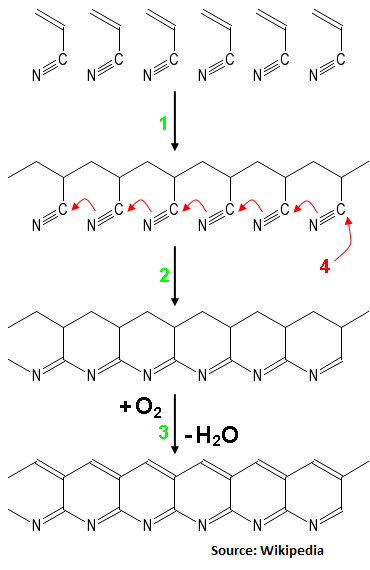
Synthesis of Carbon Fibre from Polyacrylonitrile (PAN):
Polymerization of acrylonitrile to PAN,
Cyclization during low temperature process,
High temperature oxidative treatment of carbonization (hydrogen is removed).
After this, process of graphitization starts where nitrogen is removed and chains are joined into graphite planes.
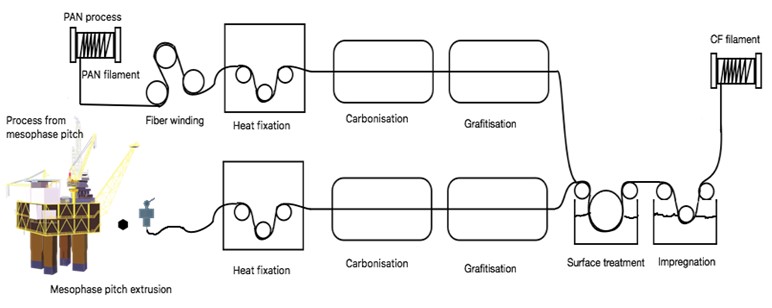
Carbonization is heat process where all the non-carbon elements are removed from the fibre, it transforms the fibre into carbon fibres at temperatures as high as 2100 °C with inert gas as Ar and N2
Graphitization is the last process that is not necessary only if you want fibres that are 99% and more carbon in the fibre. The temperatures at this point rise to 2500-3100 °C.
If We Look at the Structure of Fibres We Have 2 Types of Carbon Fibres:
- Isotropic carbon fibres with 90% of carbon with glass structure and crystal properties
- Anisotropic carbon fibres have graphite structure
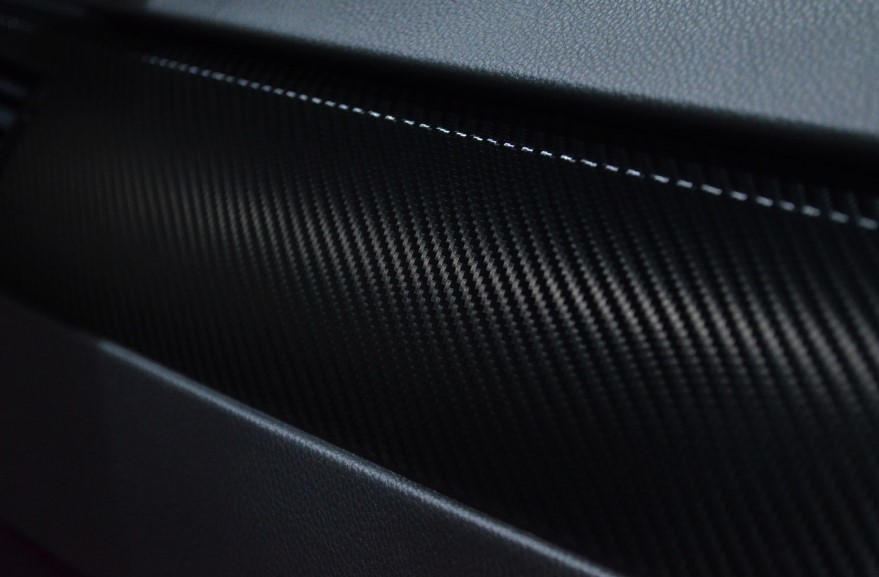
Carbon fibres have characteristic black colour and they are round cross section
Main properties of carbon fibres:
- Chemically inert high resistance to acids, alkalis and organic solvents
- High temperature resistance
- Electrical conductivity
- Moisture resistant
Carbon fibres are fragile but hard, that’s why they are mostly used with resins and in composites.
Largest manufacturer of carbon fibres is ToraycaR
Some Famous Market Names are:
- Carbofilex (Ashland, US)
- Celion and ThornelR (Union Carbide, US)
- GrafilR (Grafil, US)
- TenaxR(Tenax, DE)
(769)