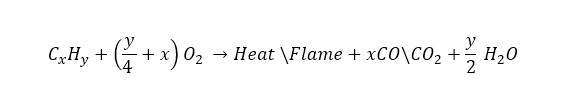Fire Fighter Suits
Protective Textiles Introduction
Fire Fighter Suits
Firefighters perform diverse tasks like firefighting, aircraft fires & other vehicle fires, wildland firefighting etc. Firefighters garments should be designed considering some functions, the most important of which is protection against heat & flame. And protection against moisture is also important depending on the type of extinguishing method.
Firefighters suits first appeared and used in 1930s and were originally made of asbestos fabric. Today this suit is made from vacuum-deposited aluminized materials.
There are three basic types of this aluminized suit:
- Approach suit: ambient heat protection up to 200° F(93°C) and used for work in the general area of high temperature such as steel mills.
- Proximity suit: kiln ambient heat protection up to 2000° F(1093°C) and used for aircraft rescue and firefighting etc.
- Entry suit: ambient heat protection up to 2000° F (1093°) and used in the situation in which requiring protection from extreme heat.
Thermal Environment Faced by Firefighters
Uncontrolled fire hazard starts with ignition of at least one combustible substances and that is usually organic hydrocarbon or cellulose that contain carbon, hydrogen or oxygen. General combustion reactions of this substances are –
This generates visible luminous flame which creates a thermal environment of a certain intensity in the surrounding with fire hazard. In such variable temperature and heat condition firefighters have to perform various job activities such as extinguishing the fire, rescuing fire victims and property etc.
Structure of firefighter suit
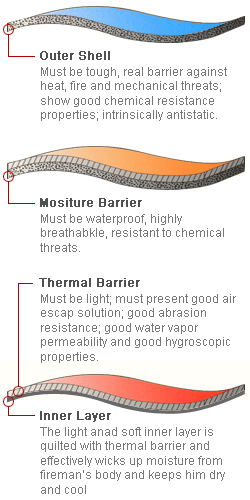
Firefighters suits are made from three ply of fabric:
This fabric is made of flame resistant material. Outer layer fabric may be made from aramid fiber, blend of aramid and novoloid fiber or FR cotton. For the three ply woolen fabric this layer may be made of wool serge which is fine but densely woven.
(Novolac: high thermal and flame resistance fiber, 85% cross linked novolac, phenol formaldehyde)
2 . Middle ply fabric:
This fabric should be vapor or moisture barrier. Middle layer is coarse and brushed woolen. It is coated to the inside of outer shell fabric as well as is a light weighted knitted material or web. This layer is obligatory in some countries, whereas in some coun- tries firefighters prefer suits without moisture barrier because of their thermal comfort.
3 . Inner ply fabric:
This layer of fabric should be thermal barrier and may be made of light weight cotton fabric. It can be consisted of a spunlaced, non- woven felt or laminated to a woven lining fabric. The thermal liner prevents the transfer of heat from environment to the body.
The effectiveness of the clothing is related to thickness of the clothing. Higher the thickness of the clothing better the effective- ness of the clothing as firefighter suits. But it should be keep in mind that excessive thickness will be trouble for the user due to heavy weight of the suit.
Protective Textiles Introduction
(2261)