Carding Introduction | Part 01
Part 01 | Carding Introduction | | Part 02 | Carding Action
Part 03 |Card Clothing | Types of card clothing | | Part 04 | Auto Leveling in Carding
Part 05 | Measuring Devices in Carding | | Part 06 | Characteristics of Card Sliver
Carding | Types & Parts of Carding Machine | Working Principle of Carding Machine
Carding: Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermix fibers s to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. In this process fibers are opened, parallelized & removes dust, impurities, short fibers to produce continuous strand of sliver. This is achieved by passing the fibers between differentially moving surfaces covered with card clothing. The word is derived from the Latin “CARDUUS” meaning thistle or teasel, as dried vegetable teasels were first used to comb the raw wool.
Objectives of Carding:
There are many objectives of the carding process and these can be summarized as:
- Opening the tufts into individual fibers
- Eliminating all the impurities contained in the fibers
- Extracting of neps
- Fiber blending & orientation
- Removal of short fibers
- Parallelizing and stretching of the fibers
- Transformation of the lap into a sliver
All the above purposes have explained in the following:
- Opening the tufts into individual fiber: Card opens the tufts into the stage of individual fibers , whereas the blow room only opens the raw materials into flocks. This is essential to enable the elimination of impurities and performance of the other operation to be achieved.
- Elimination of impurities: Elimination of the impurities of the fiber is mainly done in taker in zone. The degree of cleaning achieved by the modern card is very high, in the range of 80-95%. The overall degree of cleaning efficiency by the blow room & carding together is 95-99%., but carded sliver still contain 0.005-0.3% foreign matters.
- Elimination of Dust: The card also removes a large quantity of micro particles that are bound to the fibers produced in the blow room. Card is considered as the best dust removing zone.
- Removal of short fiber: Very small or fewer than 10% short fibers are removed from the card. Those short fibers can only be removed if those are pressed into the clothing.
- Blending of fibers : Intimate fibers with fibers mixing is achieved here for the formation of web and repeated rotation of the fibers in the main cylinder. It should be noticed here that, carding is the only machine for processing the individual fibers.
- Fibers orientation: It is often attribute the effect of parallelizing. The card can be given the task of creating partial longitudinal orientation of the fibers.
- Formation of sliver: The main output of carding is sliver. Here sliver is formed to deposit the fibers material for further operation. It also done to transport from blow room to draw frame process.
Carding is The Heart of Spinning:
It’s one of most important process in the spinning mill. It is directly determines the final features of the yarn. In carding process, fibers are opened individually; more dust & impurities are removed here. Parallelizing & stretching of fibers are also done here. Fiber orientation & transformation of fiber into sliver are also done here. Since, all the major qualities of yarn are gained here, that’s why carding is called the heart of spinning.
Different types of carding machine:
- Roller and clearer card
- Stationary flat card
- Revolving flat card
Stationary flat carding machine: In the flat carding machine the flat does not rotate and the flat covers one fourth of the cylinder.
Revolving flat carding machine: The flat revolves or rotates along with the cylinder in the Revolving flat carding machine.
In the era of modern science the carding machine also discovered new and easy to use by depend on setting and setup the cylinder and take in. Out modern carding machine gives us extra care about the fibers and make them more smooth and useable. The another different design and style carding machines are
- Dual carding machine
- Mono or single carding machine
- Tandem carding machine
1 . Mono Carding machine: When a single carding machine with one cylinder is sued for carding, it’s called Mono carding machine. It is used for cotton, not successful for jute.
2 . Dual carding machine: When two individual carding machine i.e. breaker card and finisher card are used in carding, they are called dual carding machine. It is used for jute processing.
3 . Tandem carding machine: When tow carding machines are used at a combination then it is called Tandem Carding machine. The motion is transferred from 1st machine to the 2nd machine. When one machine stops the other stops automatically. It is sued in case of Roller spinning in Cotton.
In tandem carding machine, two individual cards make up a unit. The doffer of the 1st card feeds fibers material to the taker-in of the 2nd card. Double carding of the raw material has a positive effect on quality and on blending. However the advantage is obtained at high cost hardware and maintenance. Again additional space is required for tandem card. About 1% cotton is processed with tandem cards now. Modern cards are considered as a tandem of the latest generation.
Working principle of carding machine:
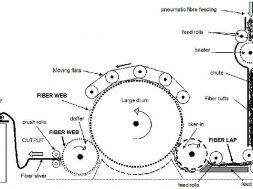
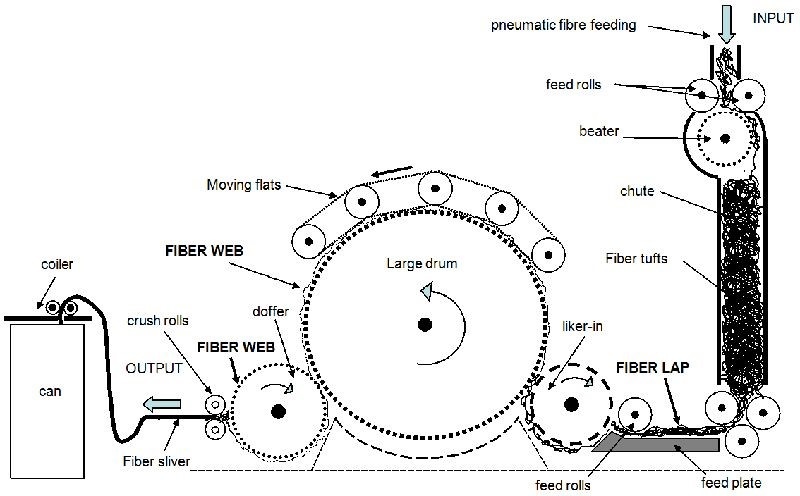
Fig: Parts of carding machine
Parts of Carding Machine:
- pipe ducting
- feed chute
- transport roller
- feed arrangement
- taker-in/licker-in
- grid equipment
- suction duct
- main cylinder
- fixed carding bars
- flats
- Cleaning unit
- Fixed carding bars
- Cover plates/grid
- Doffer
- Stripping device
- Calendar roller
- Cans
- Coiler
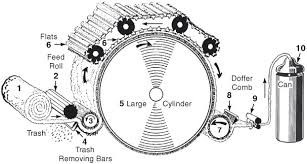
Material Passage Diagram of Carding Machine
Fig: Material passage diagram of carding machine
1 . Feed roller- taker in zone: From the feed arrangement, the chute mat is pushed into the working zone of the feed roller-taker in. The chute mat is opened to tufts by the taker in wire through combing action.
2 . Taker in-cylinder zone: From the feed roller-taker in zone, the opened tufts are transferred to the taker in-cylinder working zone for opening to small tuft size. For cleaning, the material is passed over grid equipment and mote knife attached the underside of taker in. Here points are in face to back arrangement. Suction ducts carry away the waste from trash box.
3 . Cylinder-Flat zone: The small tufts are then transferred to cylinder-flat zone and opened up into individual fibers which are defined as the actual carding process. Here points are in face to face arrangement. Neps are removed in this zone. The flats comprise 80-116 individual carding bars combined into a belt moving on an endless path and approx. 30-50 flats are active to the main cylinder. The rest are on the return run. During this return, a cleaning unit strips fibers, neps and foreign matter from the flat bars.
4 . Cylinder-doffer zone: After the carding operation, the cylinder carries along the fibers s that are opened to single and loose condition as well as lie parallel without continuous structure. For the purpose of forming a continuous structure of the carded single fibers s the doffer is required. The doffer combines the fibers s into a web. Here points are in face to face arrangement.
Part 01 | Carding Introduction | | Part 02 | Carding Action
Part 03 |Card Clothing | Types of card clothing | | Part 04 | Auto Leveling in Carding
Part 05 | Measuring Devices in Carding | | Part 06 | Characteristics of Card Sliver
(11607)