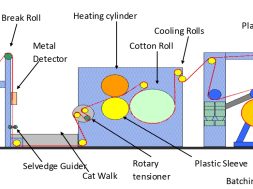
Introduction to Sizing of warp yarns
Introduction to Desizing of Warp Yarns
Introduction to Sizing of Warp Yarns
Textile Sizing :
The process of applying a protective adhesive coating upon the yarn surface is called textile sizing. This is the most important operation to attain maximum weaving efficiency specially for blended & filament yarns. Different types of sizing are used like Starch, Modified starch, polyester, polyacrylates, polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate, CMC etc.
Objective of sizing :
The main objective of sizing is to form a uniform layer of protective coating over warp yarn and lay down protruding fibers that project out of its surface.
Importance of sizing :
A film of size not only protects neighboring warp yarns on a weaving machine from getting entangled through formation of globules of fibers while rubbing against each other, but it also improves the work of rupture of yarn, which is crucial for withstanding weaving strains.
A size recipe depends not only on the nature of warp yarns, but also on weaving conditions.
Sizing Materials : The principal components of a sizing materials are:-
- Adhesive
- Lubricant
- Antimicrobial agents
The components are mixed into a slurry in a preparatory section and supplied to the sizing box of a sizing machine in a controlled manner. Preparation of the sizing slurry varies according to the composition of the sizing material and may or may not involve heating
In order to hold down protruding fibers onto the yarn body, the number of bonding sites between the sizing material and the fibers constituting the yarn must be sufficiently high. The weaker the bond strength between the sizing material and the fibers, the larger the number of bonding sites must be. A sizing material should ideally have a low bond strength as it has to be disposed of after sized yarns have been woven into a fabric. Strong bonds not only cause problems during size removal, but also involve unnecessary expenditure. So a suitable optimization between the adhesive power of sizing adhesives and ease of removal has to be worked out.
Starch as a Suitable Material for Sizing Cotton :
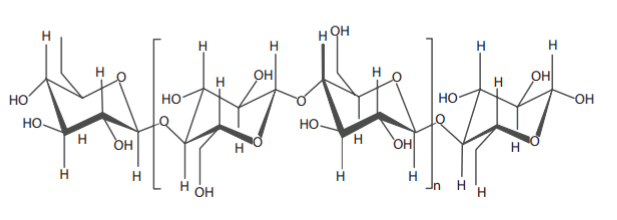
The bonding of chemical groups of a cellulose unit of cotton is shown in the following figure.
It is clear from the figure that cotton has a number of −OH groups, which are potential groups for H-bonding. Hence, an adhesive material for sizing cotton should have the following characteristics:
- High degree of polymerization
- Large number of −OH groups
- Ease of removal
Considering natural materials, it is observed that some polysaccharides available in abundance satisfy these criteria. These are namely cellulose, gums, and starches.
Starch is usually composed of two components, a straight chain polysaccharide of glucose and a branched chain polysaccharide of glucose. Amylose, the straight chain component, is relatively low in molecular weight, water soluble, and makes up to 20%–30% of starch, and amylopectin, the branched chain component, is relatively high in molecular weight, water insoluble, and makes up 70%–80% of starch.
Sizing of Synthetic Fibers :
Synthetic fibers and yarns pose a very different problem in sizing. The basic problems associated with sizing of synthetic yarns arise out of the following issues:
- Absence of −OH groups
- Hydrophobicity of material.
sizing of hydrophobic yarns, one has to primarily depend on the following forces:
- Vander Waals forces
- Dipole–dipole forces.
Adhesive material characteristics :
- Adhesive molecules must be as linear as possible.
- Adhesive material should have favorable dipole–dipole interacting (polar) groups.
Introduction to Desizing of Warp Yarns
(1344)