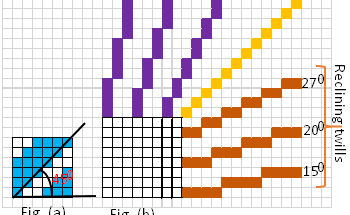Study of Twist | Twist in yarn | Introduction of twist in yarn
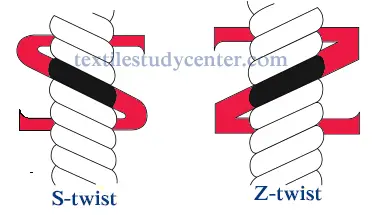
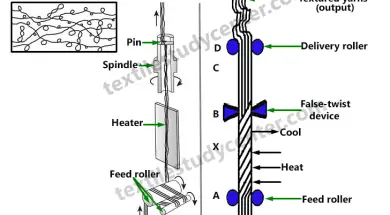
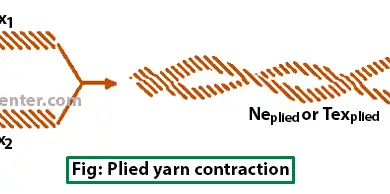
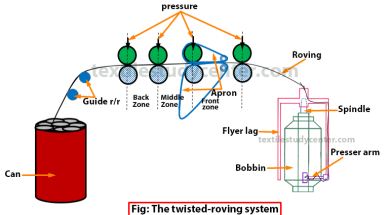
0shares Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Tumblr Digg Print Reddit Weibo Xing Blogger MySpace Study of Twist in spinning | Twist in yarn | Introduction of twist in yarn Definition of twist: The term “twist” defines the helicoidal or spiral configuration organized by the rotation of a yarn or of a bundle of fibers around their […]