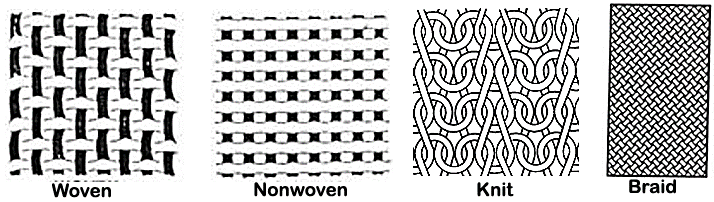
Woven fabric Structure
Woven fabric Structure
Structure
The order of interlacement of warp and weft threads at right angles is known as structure of woven fabrics. The interlooping system of yarns is known as structure for knit fabrics.
Foundation of woven cloth structure
Variation of woven cloth structure depends on following foundational factors:
The nature of yarns used.
The count or relative thickness of the yarns used as warp and weft
The order of interlacing the ends and picks
Thread density of a fabric
Modifications produced by finishing
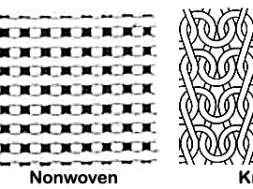
Classification of fabric structure
❶ Woven fabric structure
❷ Knit fabric structure
❸ Non-woven
❹ Braid

Woven Fabrics
Woven fabrics are defined as fabrics composed of warp yarns (Iongitudinal) and weft yarns (transverse) that are interlaced at according to the type of weave or design that are desired.
Classification of woven fabric structure
Woven structures are classified into the following categories:
❶ Simple structures
❷ Compound structures
Simple structure
Only one series of warp (end) and one series of weft (pick) threads are used in this construction.
The warp and weft threads are interlaced with one another at right angle.
All the neighbouring warp and weft threads are parallel to one another and play an equally important role in determining the properties of the fabric.
Example: Plain, Twill and Satin fabric.
Compound structure
More than one series warp and weft threads are used in this construction.
Some of threads forms the body or ground and the other forms the figuring or ornamentation.
The neighbouring threads need not be parallel to one another.
Example: Pile, Towel fabric
Texture
Texture refers to surface variations in fabric that can be used as an effective element of design. Fiber type, yarn structure, fabric construction, and fabric finishes can create infinite varieties of texture. The range of textures produced in plain cloth is wide. The plain weave is produced in a variety of forms and textures. A variety of forms in textures are produced:
By causing a differential tension between the warp threads during weaving.
By using various counts of yarn for weaving different types of fabrics.
By using warp and weft yarns of different counts in the same fabric.
Methods of fabric representation
A weave is the interlacing pattern of the warp and weft. There are two ways of interlacement.
❶ Warp overlap in which warp is above 101meds weft

❷ Weft overlap in which weft is above warp

When the warp is lifted above the inserted weft, a warp overlap is obtained. When the warp thread is lowered, the weft thread is inserted above the warp thread and the weft overlap is obtained.
Important definitions
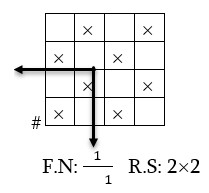
One repeat of weave : A number of inter lacings combined together in both direction produces a unit of design and one repeat of weave.
Formula number : Any structure or interlacement represent as a small fraction is known as formula number.
Repeat number or repeat size (R.S) : No. of warp yarn and no. of weft yarn in a repeat is known as warp repeat no. and weft repeat no.
Basic element of a woven design
Woven Fabric design is represented by the following plans.
❶ Weave plan
❷ Drafting plan
❸ Lifting plan/ Peg plan
Weave plan:
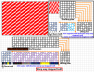
The weave plan is the representation of the interlacement of warp and weft yarn in the woven fabric. A blank in a square indicates that a warp goes below the corresponding weft and any color or ‘X’ mark in the square indicates that the warp floats above the weft.

Features of a design or weave plan
The vertical lines or space is represented as a warp.
The horizontal lines or space is represented as a weft.
One complete repeat should be shown on design paper.
Each square indicates an intersection of a warp and a weft.
‘X’ mark or color represents warp over weft.
Blank square represents weft over warp.
# indicates starting point.
![]() symbols indicates repeat unit.
symbols indicates repeat unit.
(10218)