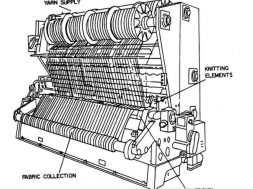
Motion of Loom
Types of Motion of Loom
In order to interlace wrap and weft threads to produce a fabric, the following motions are necessary on any type of loom:
[In Shortly]
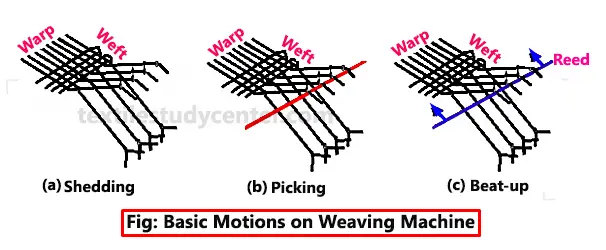
❶ Primary motions of loom :
Shedding: Dividing warp threads into two groups.
Picking: Insertion of weft through the passage created.
Beating: Pushing the newly inserted weft yarn into the cloth fell/ already woven fabric.
❷ Secondary motions of loom :
Let off motion: Causes unrolling of warp from the warp beam.
Take up motion: Causes rolling of the cloth roller and cloth.
❸ Tertiary motions of loom :
Warp stop motion, Weft stop motion, Warp protector motion,Weft mixing motion, Feeler motion, Break motion, Weft replenishment motion etc.
Primary motions of loom :
Primary motion is necessary for weaving fabric. Without this mechanisms, it is practically impossible to produce a fabric. For weaving a fabric, three primary motions are required in the loom.
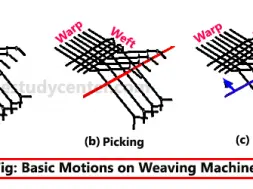
❶ Shedding: Shedding is the operation by which the warp is divided into two sheets so that sufficient gap is created for the uninterrupted passage of the weft from one side of the loom to the other.
❷ Picking: Picking is the operation to transfer the weft yarn (pick) into the shed from one side of the loom to the other. In shuttle loom, picking is done from both sides of the loom. However, in shuttle less looms, it is done from only one side of the loom.
❸ Beat up: Beat up is the operation of pushing the newly inserted weft yarn back into the cloth fell by using the reed.

Secondary motions of loom :
Let-off motion:This motion delivers warp to the weaving area at the required rate and at a suitable constant tension by unwinding it from a weaver’s beam.
Take-up motion: This motion withdraws fabric from the weaving area at the constant rate that will give the required pick spacing and then winds it onto a roller.
Auxiliary motions of loom :
Auxiliary motions are added to a loom to get high productivity and good quality of fabric. These motions are useful but not absolutely essential. They are….
Warp stop motion: This motion able to stop the loom when a warp thread breaks or get excessively loosened.
Weft stop motion: This motion able to stop the loom when a weft breaks or runs out of the pirn (weft package).
Warp protector motion: This motion protect the warp threads by stopping the loom when the shuttle fails to reach, the selvedge side and box properly into either the shuttle box during picking.
Weft mixing motion: This motion able to insert various coloured weft yarn into the same fabric for check and stripe effect.
Feeler motion: This motion able to indicate whether the weft yarn in pirn is almost used up or not.
Brake motion: A mechanism to stop the loom when a weft yarn breaks.
Weft replenishment motion: This motion provide uninterrupted filling insertion by switching from a depleted to a full package.
(18985)