Tuck Stitch and it’s Formation Process
Tuck Stitch and it’s Formation Process
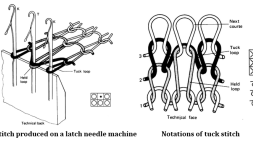
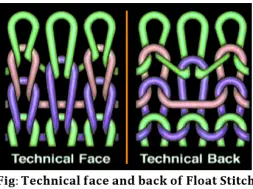
Tuck Stitch
Features of tuck stitch
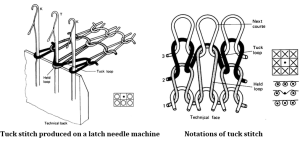
►A tuck stitch is composed of a held loop, one or more tuck loops and knitted loops.
►It is produced when a needle holding its loop (T) also receives the new loop, which becomes a tuck loop because it is not intermeshed through the old loop.
►The tuck loop thus assumes an inverted V or U-shaped configuration.
►The head of the tuck is visible on the reverse of the stitch.
►The side limbs of tuck loops thus tend to show through onto the face between adjacent wales.
►Tuck stitch structures show a faint diagonal line effect on their surface.
►In analysis, a tuck stitch is identified by the fact that its head is released as a hump shape immediately the needle loop above it is withdrawn.
►A knitted loop would be required to be separately withdrawn
Tuck stitch formation
Effect of tuck stitches
►Fabric with tuck stitches is thicker than knit stitches due to accumulation of yarn in stitches at tucking places.
►The structure with tuck stitches is wider than with knit stitches as the loop shape has a wider base.
►As the loop length is shortened, the tuck stitched structure is less extensible.
►Due to thicker in nature, the tuck stitched fabric is heavier in weight per unit area than the knit stitches.
►Tuck stitched structure is more porous and open than the knit stitched fabric.
►Tuck stitch is also used to get fancy effects by using colored yarns.
►Tuck loops reduce fabric length and length-wise elasticity because the higher yarn tension on the tuck and held loops causes them to rob yarn from adjacent knitted loops.
►Fabric width is increased because tuck loops pull the held loops downwards, causing them to spread outwards and make extra yarn available for width-wise extensibility.
►Fabric distortion and three-dimensional relief is caused by tuck stitch accumulation, displacement of wales, and by varying numbers of tuck and knitted stitches per wale.
►The tuck stitch may also be employed to produce open-work effects, improve the surface texture, enable stitch-shaping, reinforce, join double-faced fabrics, improve ladder-resistance and produce mock fashion marks.
(2991)