Fundamentals Of Warp Knitting | Warp Knitting Elements
Fundamentals Of Warp Knitting
Warp Knitting :
- Warp knitting is defined as a loop forming process in which yarn is fed into knitting zone , parallel to fabric selvedge .
- In warp knitting , fabric is made by forming loops from yarns coming in parallel sheet form run in the direction of fabric formation . ( warp beam like in weaving )
- So that warping process is essential for warp knitting .
- Every needle is fed by a separate yarn for loop formation . In order to connect the loops into a fabric , the yarns are shifted between the needles .
- All the yarns will be knitted in course simultaneously.
- For the purpose of shifting yarn , guide will be used.
Warp knitting machines are flat and comparatively more complicated than weft knitting machines.
Basic Warp Knit Structure :
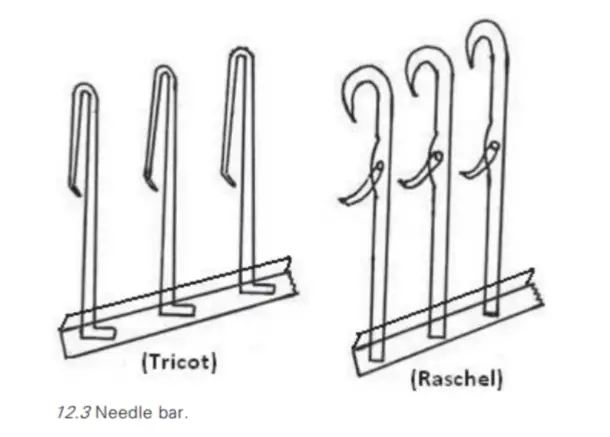
Needles and needle bar :
- In a warp knitting , all the loops in a course are made simultaneously . (vice versa to weft knitting )
- So that instead of giving motion to individual needles , all the are connected to bar is called needle bar .
- It will be lifted up and lowered down by means of a cam fitted outside the machine .
- Mostly in the warp knitting machines bearded and latch needles will be used.
Pressure Bar :
- Its essential when the warp knitting machine using bearded needles for closing the hook of the needle.
- When the hook is closing , the old loop will be cast-off from the needle.
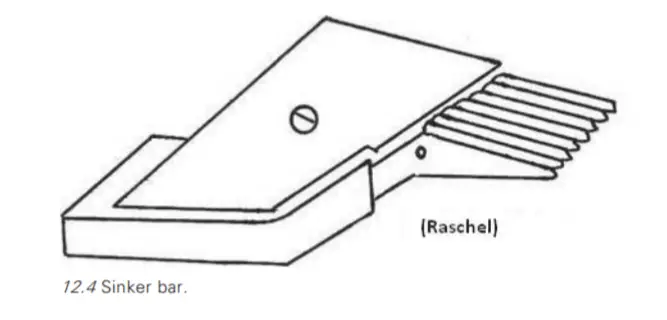
- The sinker is thin plate of metal which is placed in between two needles .
- The sinkers are almost have forward and backward direction through the sinker bar .
- The sinkers were driven by crank or eccentric arrangement .
- The throat of the sinker will be used to holding the fabric while the needles lifted up
Guide and Guide Bar :
- Guides are the metal plates drilled with a hole in their lower end.
- The guides are held together at the upper end in a metal is called guide bar. The guides are placed in between two adjacent needles .
- Guides are evenly spaced , similar to the gauge of the machine.
Knitting Terms :
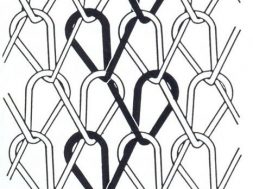
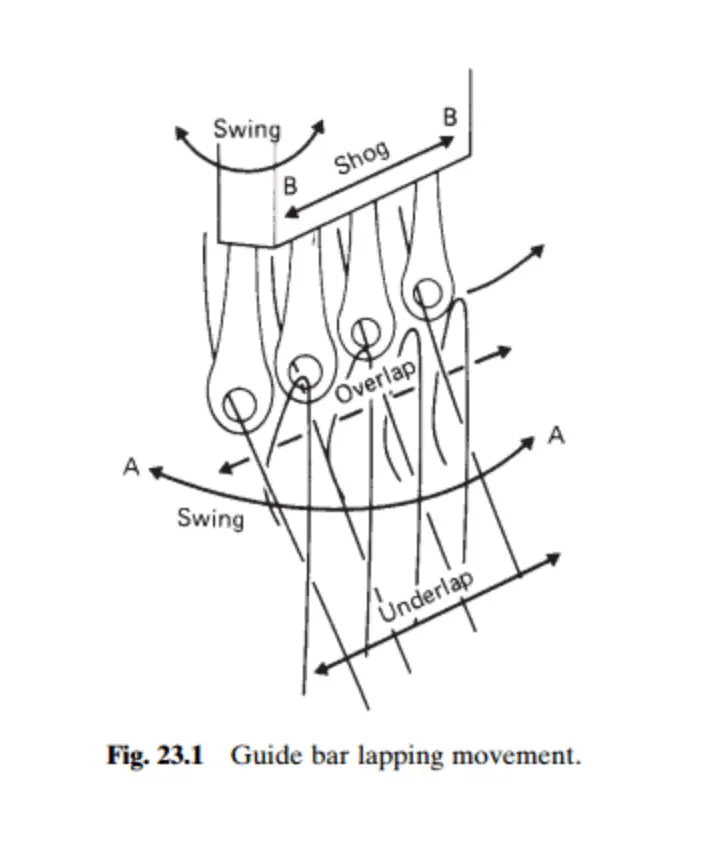
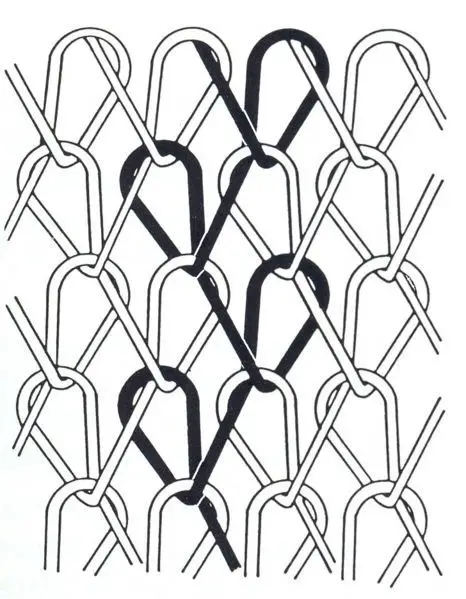
Over lap :
Loop formed by the yarn is called overlap.
Under lap:
Length of yarn connecting the loops is called underlap. Otherwise two successive over lap connected by the yarn , that length of yarn is called underlap.
Open lap :
Its formed when the over lap and next under lap is formed in the same direction.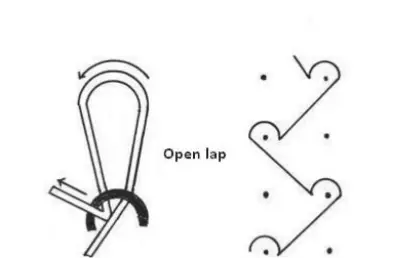
Closed lap :
It is formed when the over lap and the following under lap is formed in the opposite direction .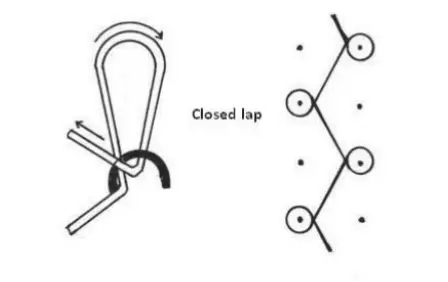
GUIDE BAR MOVEMENTS :
1 . In order to feed the yarn to the needle for loop formation as well as to connect the adjacent wales , the guides of a guide bar are required to execute a compound lapping movement .
2 . There two two movements of guide bar in a knitting machine.
Swinging movement
Shogging movement
3 . The swinging and shogging motion act at right angle to each other in order to form overlap and underlap .
4 . The swinging motion of guides takes place either from front of the needles to back or back of the needles to front . it is in arc and it occur between adjacent needles .
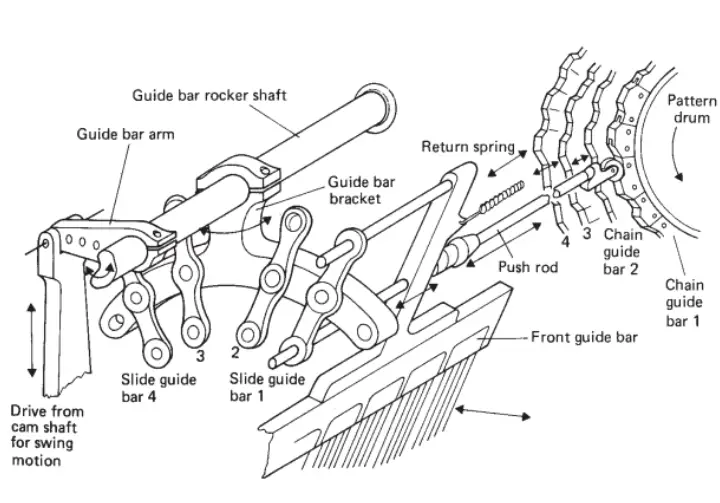
5 . The motion will be derived from the main cam shaft and it passes motion to guide bar via levers , pivots and linkages .
6 . The one end of the guide bar arm is lifted up and lowered down , the other end of the same connected to the rocking shaft causes angular movement on the rocking shaft .
7 . Due to the angular movement of the rocking shaft , the guide bar arm also move front and back and vice versa .Ultimately the swinging motion of guide bar will be achieved .
8 . The shogging movement of guide bar is the lateral movement of guides which is parallel to the needle bar. The shogging motion of guides either left to right or right to left.
9 . The extent of shog may vary from cycle to cycle .
10 . The occurrence , direction , timing and extent of each shog is separately controlled for each guide bar by using pattern chain links or pattern wheels . ( such as similar to pattern cylinder in dobby loom )
11 . We can use more than one guide bar .
12 . When using more than guide bar , it gives new option for designing .
13 . Underlap will be decided by the guide bar movement .
14 . The guide bar motion is expressed in terms of needles . ( one needle movement , two needle movement )
15 . When two guide bars have different motion during the knitting cycle the let off mechanism for both will be different . because yarn consumption will be vary.
The above types of chain link mounted on the pattern drum depending upon the structure of the fabric .
(5680)