Work Study | Method Study | Part 02
Part 01 :Industrial Engineering | Responsibilities of Industrial Engineers (IE) | How to conduct Time Study
Part 03 : Line Balancing | How to Balance a Traditional Sewing Line | Tools required for line balancing
Part 04 :Work Place Layout for Garments | Checklist for Work Station Design | Basic Guide to Work Place Layout
Work Study | Parts of Work Study | Method Study | Techniques of Method Study
Work Study:
Work Study is the systematic examination of the methods of carrying out activities such as to improve the effective use of resources and to set up standards of performance for the activities carried out, used in the examination of human work in all its contexts, and which lead systematically to the investigation of all the factors which affect the efficiency and economy of the situation being reviewed, in order to effect improvement.
This has to do with Productivity Improvement, but also improvement of Quality and Safety.
- The means of continuous improvement.
- The strategy of elimination waste.
- Path for productivity use of resources.
- Enhance quality of work life.
- Maximum results with minimum effort.
- Work Smart not hard.
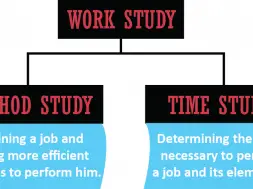
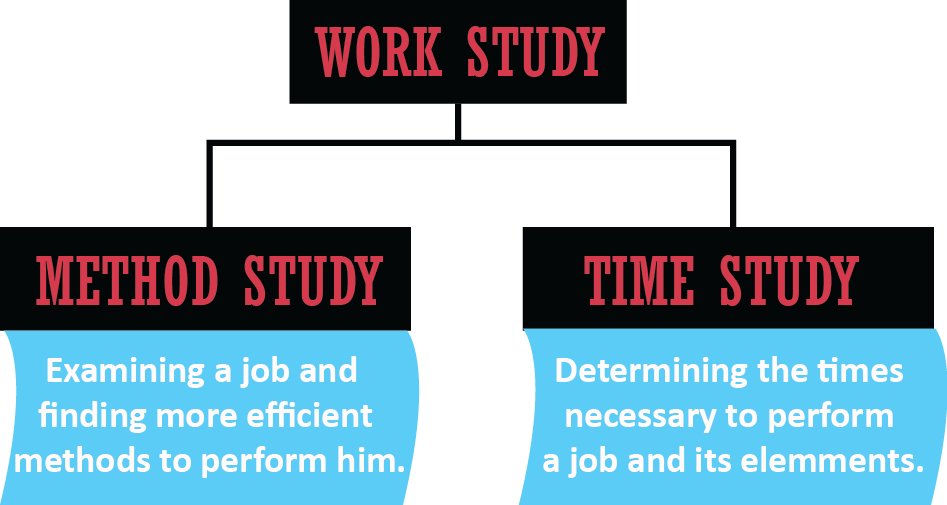
Parts of Work Study:
Work Study has two parts which are –
- Method Study.
- Time Study or Work Measurement.
Method Study
Systematic recording & critical examination of ways of doing things are in order to make improvement. According to BRIGADIER K. PENNATHUR, “method study is a systematic and scientific evaluation of existing or proposed plan and performance of any work system and the evaluation of improvement through analytical process of examination”.
Objectives of Method Study:
- For getting better equipment, decoration and design of building.
- For getting developed factory and nice office.
- For getting better working atmosphere.
- For getting developed work flow.
- For the benefit of security and health of the employees.
- For getting quality product.
- For getting quantity product.
- For getting sufficient stock of raw materials.
- For job satisfaction of employees.
- For confirmation of more profit.
- For creating new or better product with additional facilities.
- For buyer satisfaction or pre-condition.
- To utilize materials as maximum as possible.
- To reduce the wastage of every area of a factory.
- Better movement of goods and materials.
Steps of Method Study:
1 . Systematic & Scientific analysis:
It is systematic and scientific analysis of department or section, lay-out of machineries, transportation of goods or materials and movement of employees for developing method.
2 . Motion Study:
It is the systematic and scientific analysis of the movement of employees, movement of different parts of human being and movement of machines for developing the motion.
3 . Micro Motion Study:
It is the details and scientific analysis of the arms of the employees for developing the speed of arms and movement of the employees.
Techniques of Method Study:
Use of the human body:
- Both hand same time.
- Both hands not are idle.
- Motion of arms symmetrical &simultaneous.
- Eye & hand co-ordination.
- Order of movement – natural rhythmical.
- Hand and body motion lowest Classification.
Classification of body movement:
- Knuckle – Finger.
- Wrist – Hand & Finger.
- Elbow – Forearm, Hand & Finger.
- Shoulder – Upper arm, Forearm, Hand & Finger
- Trunk – Torso, Upper arm, Forearm, Hand& Finger.
Motion Economy – How?
- Reduce the number of motions.
- Reduce the distance moved.
- Reduce the precession.
- Reduce the eye shift.
- Simplify grasps.
- Toss dispose rather than place dispose.
- Best use of both hands.
- Encourage rhythm.
- Promote natural posture and movement.
Arrangement of work place:
- Definite & Fixed location.
- Pre-position reduce searching.
- Gravity feed.
- Tools & material -close to the workers as possible.
- Tools & materials -best sequences of motion.
- Drop delivers – where ever possible.
- Chair – height of the work place and comfort.
- Color – contrasts with that of the work & reduce eye fatigue.
Specific Sewing Room Methods -1:
- Table cut offs or extensions.
- Raising of machine.
- Special work aids.
- Mobile carts.
- Table cut outs.
- Close location of parts to needle.
- Pick up & position without searching.
- Easiest grasps of parts from the bundle.
Specific Sewing Room Methods -2:
- Get parts without looking.
- Get parts during sewing period.
- No re-position.
- Insert parts in folder with single push.
- Retain original alignment of parts while sewing.
- Resume sewing after start without pause.
- Quick turns while sewing.
- Continuous & full speed sewing.
- Dispose by throwing & without looking.
Design of Tools & Equipment’s:
- Relived holding by hand – jig, fixture, device.
- Combined tools.
- Inherent Capabilities of the finger.
- Placement of levers, crossbars hands, wheels least change in the body position.
Professional Approach to Method Study:
- Select : Work to be studied
- Record : Relevant Information and Data
- Examine : Critically
- Develop : Best Method and Workplace
- Evaluate / Measure : Results of Different alliterative solutions
- Define : New method which gives best economic return
- Install : As a standard practice
- Maintain : By regular routine check
Part 01 :Industrial Engineering | Responsibilities of Industrial Engineers (IE) | How to conduct Time Study
Part 03 : Line Balancing | How to Balance a Traditional Sewing Line | Tools required for line balancing
Part 04 :Work Place Layout for Garments | Checklist for Work Station Design | Basic Guide to Work Place Layout
(1905)