Disperse Dye for Polyester | Why called disperse dye | Application and mechanism of disperse dyes | Features of of disperse dyes
Part 1 : Disperse Dye for Polyester | Why called disperse dye | Application and mechanism
Part 3 : Auxilaries Of Disperse Dye
Why called disperse dye
Disperse dye are the smallest dye of all dyes. They are insoluble in water. When they are applied to the dye bath, they form dispersion. They are free from ionized group. So they have low solubility in water& are suitable for dyeing hydrophobic fibres.
APPLICATION
Disperse dye are mainly suitable for coloring hydrophobic fiber such as
cellulose ,
tri-acetate ,
polyamide ,
polyester ,
polyamide ,
polyacrylo nitrile etc.
They have become especially important, for polyester fibres as they are widely used as a blends with cotton, wool, or any other man made fibres . Disperse dyes are also used to color plastic jwellery, PVC rods and PVC/ PES film.
FEATURES
- Synthetic dye & free from ionizing group.
- Non soluble & molecularly disperse therefore dispersing agent is necessary for coloration.
- Fastness property specially wet & light fastness is good to excellent
- Molecular size is the smallest than other dye
- Economical
- Applied in acidic condition.
- High temperature is needed.
- Dyes are derivative of azo , anthroquinone , nitro & quinine group.
- Dye molecules contained a methyl amino sulpher group (-NHCH2SO3Na).
Dye-NH-CH2SO3Na + H2O NH2-Dye +CH2O + NaHSO3
CHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION:
Mono azo —- 50%
Anthraquinone —25%
Diazo—-10%
Others —-15%
|
CLASSIFICATION |
MOLECULAR WT |
POLARITY |
DYEING RATE |
SUBLIMATION FASTNESS |
|
LOW ENERGY |
LOW |
LOW |
HIGH |
LOW |
|
Medium energy |
Medium |
Medium |
medium |
medium |
|
High energy |
High |
High |
Low |
high |
MECHANISM OF DYEING
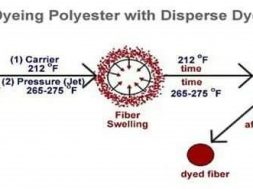
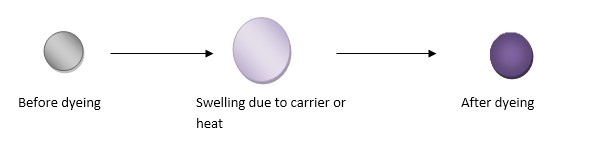
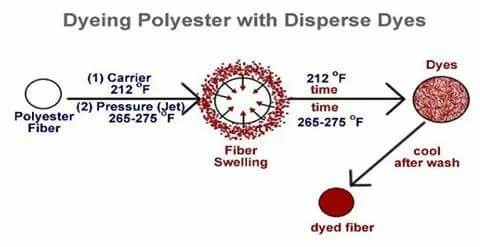
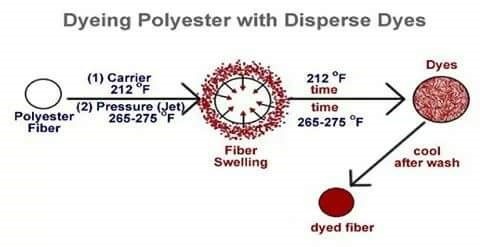
Main mechanism of dyeing is to swelling the fibre so that dye molecule gets enough space to stay inside the fibre. In hydrophilic fibre such as cotton this swelling is done by wetting. But when we dye polyester fibre , due to compact structure it is not able to swell on wetting. So it is hydrophobic fibre. Its MR% is .04% so it is highly hydrophobic. So it needs special arrangement.
Swelling is done by applying chemical or heat. The chemical which swell fibre called carrier. Heating of dye liquor swells the fibre to open up and assists the dye to penetrate the fibre polymer system. Thus the dye molecule takes its place in the amorphous regions of the fibre. Once taking place within the fibre polymer system, the dye molecules are held by hydrogen bonds and Van Der Waals’ force. When the system is taken off the molecular area shrunk & dye molecules are entrapped inside the polymer.
Polyester fibre contains pores or canals within its structure which, when heated to 100°C, expand to allow particles of the dyes to enter. The expansion of the pores is limited by the heat of the water – industrial dyeing of polyester is carried out at 130°C in pressurised equipment. Dispersal fast yellow G, fast orange G violet 2R blue GN etc are some suitable for polyester at boiling temperature without carrier.
Method of dyeing:
There are 3 methods of polyester dyeing .they are
High temperature high pressure method
Pad thermosol method
Carrier method
COMPARISION AMONG 3 PROCESS :
| PARAMETER | CARRIER | HTHP | THERMOSOL |
| Swelling | Carrier is used for swelling | temperature | Temperature |
| Temp | 90 -95*C | 130-160*C | 180-220*C |
| Time | 45 min | 60 min | 2-5 min |
| Effect on environment | Not environment friendly | Friendly | Friendly |
| Fastness | Light fastness not good | Fastness property is good to excellent | Good |
| Molecular wt of dye | Low | higher | medium |
| application |
Wool/PE |
CVC, TC | TC, POLYESTER |
Disperse Dye for Polyester
Part 1 : Disperse Dye for Polyester | Why called disperse dye | Application and mechanism
Part 3 : Auxilaries Of Disperse Dye
(5436)