Drawing Of Synthetic Fibres
Drawing Of Synthetic Fibres
Introduction:
- With the exception of silk , all the filaments are manufactured from man-made materials . silk is a natural filament.
- The man-made materials are primarily made from chemicals that must be formed and solidified into fibre form.
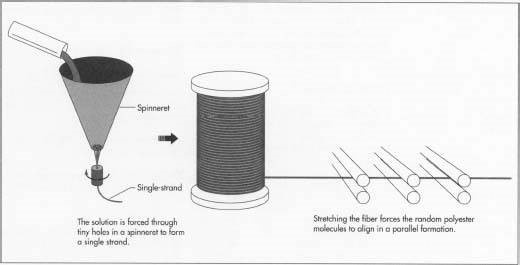
- The fibre forming polymers are normally solids and therefore must be first converted into a liquid form to be suitable for extrusion.
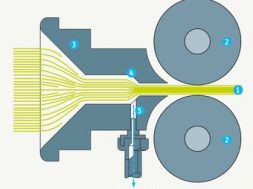
Drawing:
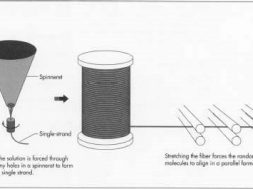
- Drawing is very important process of spinning.
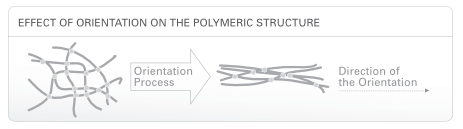
- This process used to increase the orientation of polymer molecules.
- It produce filament with desired strength.
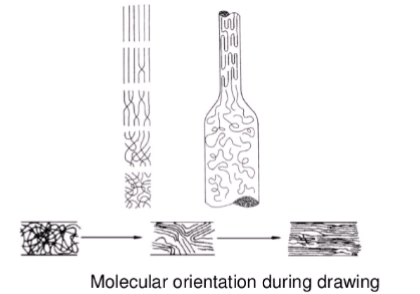
- During the drawing operation molecular chains are aligned along the fibre axis.

Undrawn fibre properties:
- Semi-crystalline
- Lamellar structure
- Amourphous region
- Low rigidity and strength but high elongation
Crystalline and strength:
- Drawing process increases tensile strength and hardness of filament.
- It orients the polymer molecules along the filament.
- Crystallinity increases due to the orientation of polymer molecules.
Properties induced by drawing:
- High degree of orientation of polymer molecules that tends to increase fibre stiffness.
- More breaking strength.
- Low moisture absorption.
- More luster and transparency.
- Fibrillar structure.
- More dimensional stability.
Objective of drawing:
- To induce the molecular orientation in the fibre.
- Thereby increasing their strength in the direction of stretch.
- Extension of the filaments to many times their original length.
Purpose of drawing:
The primary purpose of drawing of yarn is to be a desirable quality for the following reasons :
- To increase the crystalline zone in fibres.
- To produce fibres with the specific properties desired.
- To convert relatively week spun fibres to fibres with greater molecular orientation and the resulting greater strength.
- To produce filaments with a desired strength by inducing sufficient orientation of the polymer molecules along the axial direction.
Draw ratio:
The ratio between the take-up roller and the extrusion rate is known as draw ratio.
If we increase the take-up speed draw ratio will be increase.that means fibres will be stretched according to our requirement.
Types :
- Low oriented yarn(LOY)
- Partially oriented yarn(POY)
- Fully oriented yarn(FOY)
LOY : There is no orientation as well as crystallinity.
POY: There is a orientation without crystallinity.
FOY: There is a orientation with crystallinity.
|
Type |
Spinning speed |
|
LOY |
500-1500 MPM |
|
POY |
1500-4000 MPM |
|
FOY |
4000-6000 MPM |
Principle of drawing :
- The drawing process of the fibre involves passing the fibre tow over a series of rollers.
- The roller rotates at specified constant angular velocities,each faster than older.
- In some processes all the draw is introduced in one step,in a single stage of feed and take-up rollers.
This single draw can results in fibre breakage so it customary to involve more draw processes in the industries.
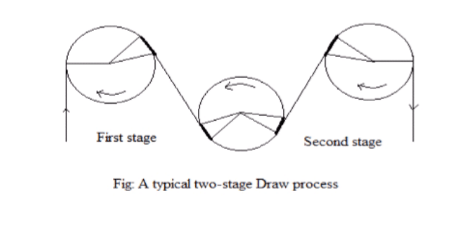
Two stage drawing process :
- In this process most of the draw was provided in the first stage ( between 2.2 and 2.7 draw ratio) and relatively smaller draw (1.1 – 1.2) in the second stage.
- As the number of stages is increased , it is possible to keep each free span and roller at a different temperature .
It induce maximum molecular orientation in the fibre.
Impact of drawing :
Fibres change in appearance as they are drawn
Example :
Nylon is usually dull and opaque , but after the drawing it will be transparency and luster.
- The more closely the molecules pack together , it has greater ultimate strength.
- Due to the increase of ultimate strength decrease in elongation before reaching it breaking point.
- More stiffness and rigidity because of molecules are packed compactly , so that resistance of movement.
- More resistance to penetration by the foreign molecules also improves resistant to chemical attack.
Errors in drawing :
There is a number of drafting stages , the results are cumulative and the range of error wavelengths can be very large.
The biggest advantage of POY :
POY are used in texturising process.
For a texturising operation POY is better than FOY. Why ?
We know that texturising is the thermo mechanical process.if we need to texturise the FOY
- Soft the material
- Then bring the form and set it.
FOY will be soft in melting point , also we have decrystallize the FOY because FOY contains more crystallization regions.
But in the POY no need for decrystallize , directly bring the form and set it . so that POY is better for texturising process.
(3230)