Garment Production System | Apparel Production System
Part 1: Garment Production System | Apparel Production System
Part 2: Progressive Bundle System
Part 3: Unit Production System | Overhead Production System | Hanger Production System
Part 4: Modular Production System | Cellular Garment Manufacturing | Toyota Sewing System
Garment Production System | Apparel Production System
Garment Production/Garment Assembly
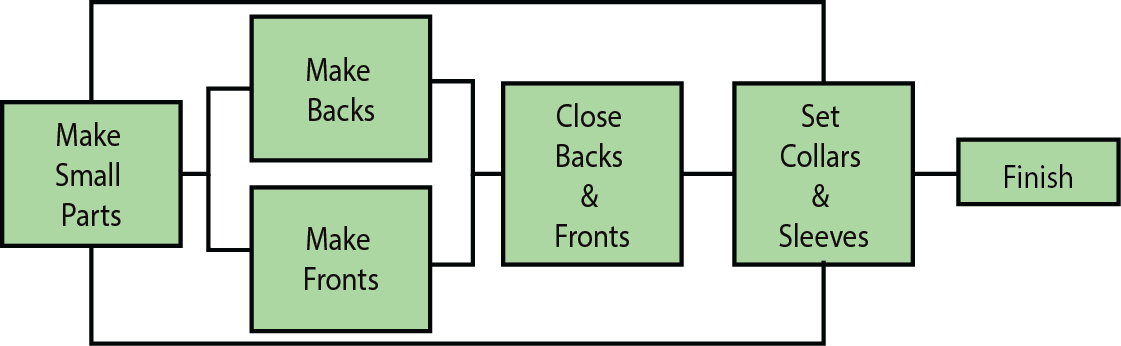
Garments assembly is a basic requirement of clothing and fashion design which involves a conversion of raw materials into a stitched and wearable piece of clothing. To make a complete garment assembling is required for different parts of a garment. The front and the back body, yoke, sleeve, collar, cuff, placket, and pocket need to be assembled together in order to make a basic shirt.
Fig: Layout & Workflow
Garments Production System
Production systems are needed to enable companies to produce the largest number of products effectively and efficiently for the lowest cost but at the required quality. Garments production system is an integration of materials handling, production processes, personnel, and equipment’s that direct workflow and generate finished products. Simply, it is a way how the two-dimensional fabric is being converted into a three-dimensional garment in a manufacturing system. Garments can be made by applying different types of system. The garment production system used by an individual or in small tailor shops is different from the systems used in the factories. Two systems are described bellows-
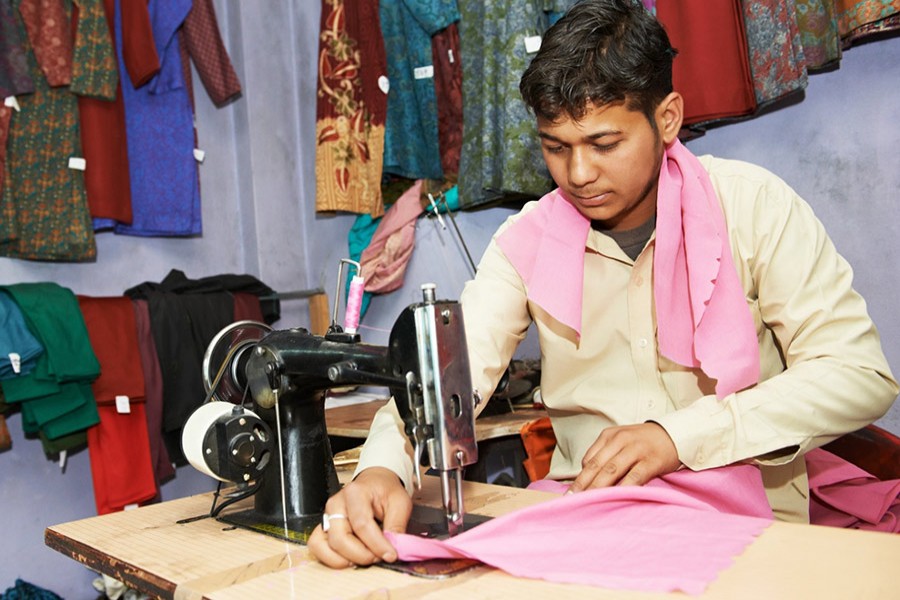
1) Individual System
It is the traditional method of production in which one operator or small team is made one complete garment at the time by carrying out all the sewing processes necessary to assemble a garment. The operator can also make a pattern and cut the fabric according to his or her own method of work. After completion of assembling one single garment, the operator will start assembling the next one and so on. This type of garment assembly system is effective when varieties of garments are required to be produced in very small quantities. The individual system of assembling garment is more common with homemakers, local tailors, boutiques, etc.
Fig: Individual System
Advantage and Disadvantage of Individual System
Advantage
It has a quick throughput time and easy to supervise.
There is no WIP in make through.
No problem of absenteeism
Disadvantages
High labour cost
Multi-skilled operator is required for assembling
Low productivity
This system is limited to couture and sample making
2) Factory Production System
When products are made in a factory, there will be a system to ensure everything runs smoothly. These are generally referred to as production systems. Several different production systems are used in the apparel industry for assembling a garment. The choice of best production system depends on the type of product, number of product to be made, when the products are needed, the size of the factory, the skills of the employees. The most commonly used types of production systems in the garment industry are:
i. Progressive Bundle System (PBS)
ii. Unit Production System (UPS)
iii. Modular Production System (MPS)
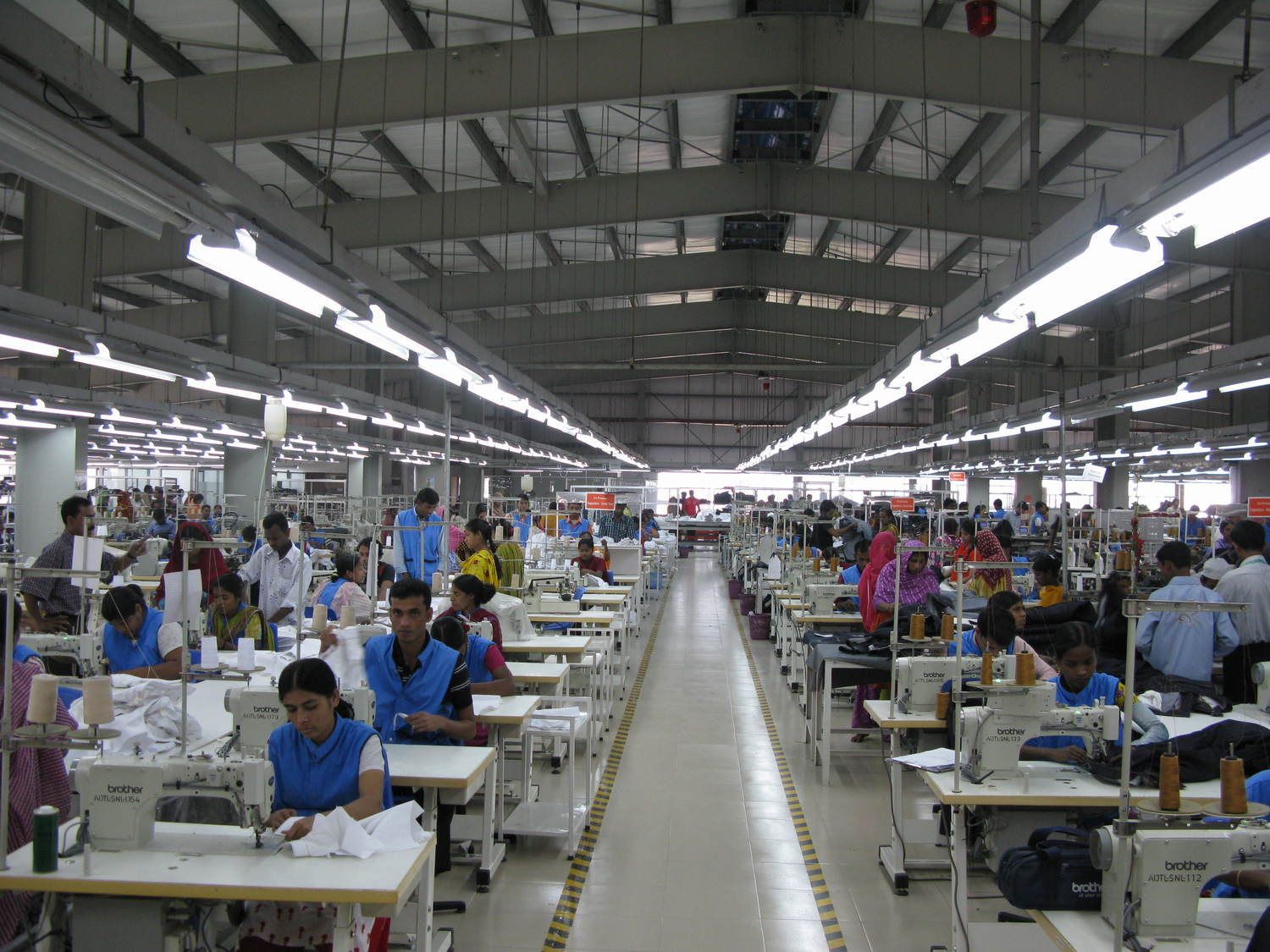
Progressive Bundle System (PBS)
The progressive bundle system is a traditional production system that has been widely used in the apparel industries for many decades and still is today. In this system bundles of garments parts are moved in sequence from one sewing machine operator to the next. Each worker receives a bundle of unfinished garments and performs a single operation on each garment in the bundle. After finished of his/her work on a bundle, they are re-tied the bundle and passed on to the next operator. Each PBS task is given a target time or “SAM” (Standard Allowed Minutes). The success of PBS depends on how the production system is set up and used in a plant.
Fig: Progressive Bundle System (Courtesy: Ananta Group)
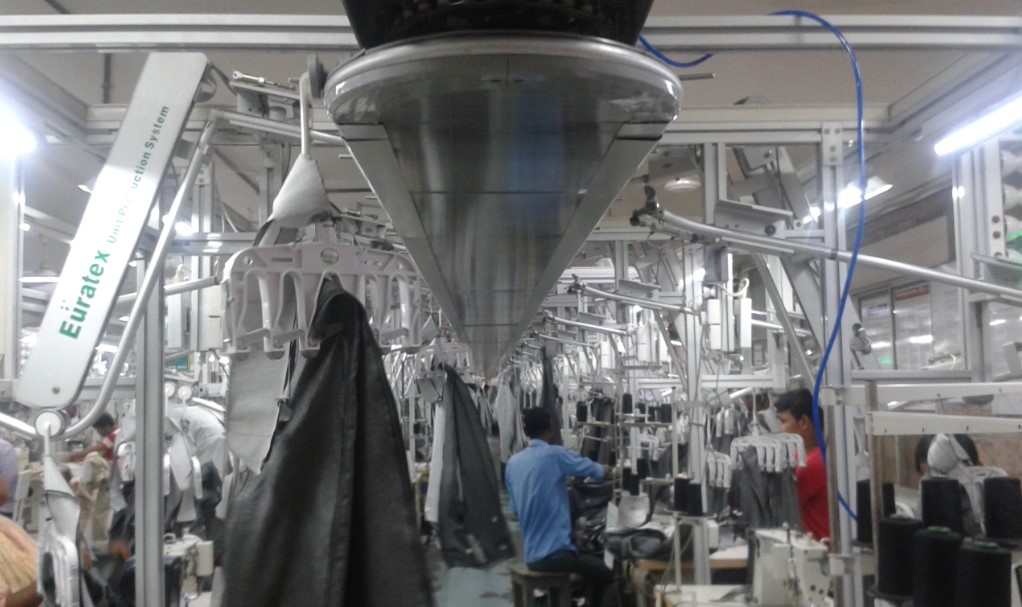
Unit Production System (UPS)
The unit production system (UPS) for apparel industries is a flexible material handling system that requires a computerized overhead transportation system to move the garment components automatically from one workstation to the next according to a pre-determined sequence. It replaces the traditional garment production system of handing, bundling, tying and untying, and manually moving garment parts. It provides uninterrupted workflow to the workers and helps to improve work efficiency and product quality. In the fast-moving fashion and apparel industry this is highly essential.
Fig: Unit Production System (Courtesy: Beximco Textile Ltd.)
Modular Production System
Modular production system involves a group of 4-17 people who set their own standards and work together to produce a finished garment. They work as a team or module and each team member works on more than one operation. In this system, operators help each other to finish the garment quickly and the team is fully responsible for the production and quality. The number of teams in a plant varies with the need of the industry, size of the industry and product line in garments. This system MPS is the perfect solution for the apparel manufacturer where quick response is needed. This system is also popular as a Cellular Garment Manufacturing, flexible work groups or Toyota Sewing System (TSS).
Fig: Modular Production System
Part 1: Garment Production System | Apparel Production System
Part 2: Progressive Bundle System
Part 3: Unit Production System | Overhead Production System | Hanger Production System
Part 4: Modular Production System | Cellular Garment Manufacturing | Toyota Sewing System
(8932)