Knitting | Knitting Types | Advantages and Disadvantages of Knitting | Properties of Knitting
Knitting
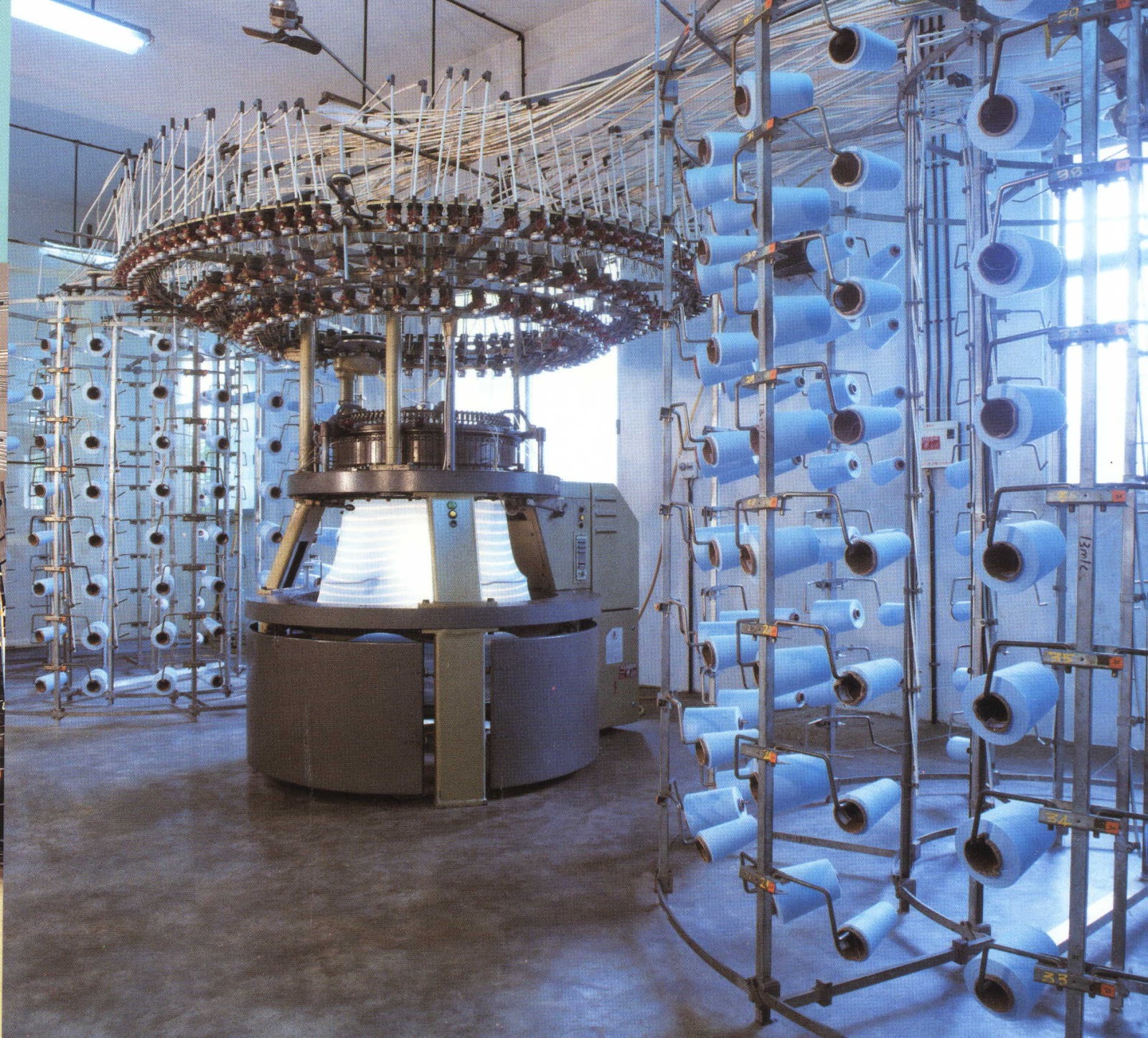
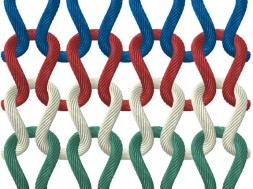
Knitting is the second most popular technique of fabric or garment formation by inter-looping one or one set of yarns. Continuous length of yarn is converted into vertically intermeshed loops either by hand or by machine. The most important parameter of a knitted fabric is loop length which can be varied during knitting by changing machine parameters, process parameters and yarn parameters. The other important parameters of a knitted fabric which are considered for assessing the quality of the fabric are courses per inch, wales per inch, stitch density, GSM and tightness factor.
Types of knitting:
- Weft knitting
- Warp knitting
Weft knitting is where the loops are formed one after another in a weft-ways direction as the fabric is formed. Warp knitting is where a set of warp yarns are simultaneously formed into loops.
Difference between warp and weft knits:
Types of weft knitting machines:
-
Flat knitting
Types of weft knitted structures:
- Single jersey structure
- Double jersey structure
- Double jersey structure:
- Rib structure
- Purl structure
- Interlock structure
Needles used in knitting:
- Bearded needle
- Latch needle
- Compound needle
Yarn preparation for knitting fabric
Knitting process will need cone, not cheese.
- Because the yarn tension maintain in the knitting will be constant. If using the cheese during the unwinding yarn will be rubbed on cheese surface.so that tension will be vary because of low twist yarn is suitable for knitting.
- Instead of using the cone unwinding will be very easy.
- During cone winding, the waxy roller will be essential because the yarn will be contacted with the knitting needles. Either the yarn will damage or the needle will be damaged.
- The cone winding machine will be run at slow speed due to the tension variation yarn will not be uniform.
- If using high speed winding machine cotton combed yarn will be better.
- Electronic yarn clearer will be used.
- Separate drive for drum and the package.
- Pneumatic splicing must be needed.
- Additive type of tensioner needed, whatever the variation in input tension output tension will be compensated by amontons law principle.
- Unwinding accelerator or the balloon breaker needed for maintaining the same tension.
Properties required for knitting:
- Flexural rigidity: Low flexural rigidity yarn can bend easily
- Torsional rigidity: When yarns are looped they are subjected to torsion yarns have low torsional rigidity will work better in knitting.
Knitting fabric properties:
| TYPE OF FABRIC | EXTENSIBILITY | ELASTIC RECOVERY |
|---|---|---|
| WOVEN | IN-EXTENSIBLE | HIGH ELASTIC RECOVERY |
| Weft knit | Highly extensible | High but incomplete recovery |
| Warp knit | Less extensible | Better recovery compared to weft knit |
Other essential properties: woven vs knits
Due to the high permeability,
- Air can be allowed into the fabric.
- Very useful in summer.
If knits are permeable, why it is preferred in sweaters for winter garments?
Because the thickness of the fabric will be more, so that more air will be drape insidethe fabric. Air is a poor conductor (thermal insulator), so that air will be heated near to body. So, our body will be warm.
Advantages of knitting:
- Fabric can be produced from minimum number of yarns, even only one yarn.
- The extensibility and stability of the fabric can be engineered.
- The desirable compactness of the fabric can be achieved easily.
- Loop structures are easily distorted under tension in application, which imparts more freedom of movement and comfort the wearer.
- Wastage of yarn during conversion of yarn into fabric by knitting is negligible.
- Knitting can produce fabrics which are very much suitable for intimate wears as well as for technical application.
- Shaping can be done at the time of knitting on the resultant fabric.
- The number of yarns to be knitted in the same fabric can be varied by selection.
- Design possibilities will be much higher.
Disadvantages in knitting:
- Dimensional stability will be lower than the woven fabric.
- Glass fabric is very critical to knitting because bending rigidity will be higher. But in the weaving we can produce glass fabric easily.
- Count range will be low in the knitting machine, but weaving is the versatile machine to produce any count of fabrics.
Reason for growth of knitting industry:
Productivity of looms at particular time
Machine productivity higher.
Labour less organised.
Floor space: Compared to auto loom for the same production
Warp knitting 1/10 th
Weft knitting 1/8 th
Power consumption: Compared to auto loom for the same production 1/4 th to 1/5 th will be required.
Yarn and yarn preparation :
- Low TPI yarns will be needed for knitting. So that spinning production will be higher.
- There is no need for warping, sizing and drawing-in processes.
- Only warp knitting need warping process.
Time required for getting an order executed is less than weaving.
Modern knitting machines particularly warp knitting machines can produce various type of technical textiles ( medical textiles, automobile textiles, geotextiles, etc.)
Computer aided designing and manufacturing in knitting have made it possible to manufacture any desired structure within a short time at reasonable price.
Knitting | Knitting Types | Advantages and Disadvantages of Knitting | Properties of Knitting
(13201)